Physical activity and quality of life
- PMID: 23412703
- PMCID: PMC3567315
- DOI: 10.3961/jpmph.2013.46.S.S28
Physical activity and quality of life
Abstract
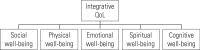
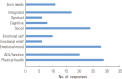
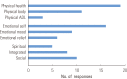
Physical activity (PA) professionals and participants recognize enhanced quality of life (QoL) as a benefit of and motivator for PA. However, QoL measures are often problematic and rarely consider the participants'perspective. This paper focuses on recent findings from a larger project on the role of QoL in PA and health promotion. More specifically, we focus on the views of participants and potential participants to better understand the relationship of PA and QoL. In earlier stages of the project we began with a conceptual model of QoL and developed a survey. We now focus on participants' views and ask two questions: 1) what is QoL? and 2) how does PA relate to QoL? We first asked those questions of a large sample of university students and community participants as open-ended survey items, and then asked focus groups of community participants. Overall, participants' responses reflected the multidimensional, integrative QoL model, but the responses and patterns provided information that may not be picked up with typical survey measures. Findings suggest that PA contributes to multiple aspects of QoL, that social and emotional benefits are primary motivators and outcomes for participants, and that the meaning of QoL and PA benefits is subjective and contextualized, varying across individuals and settings. Programs that directly target and highlight the multiple dimensions and integrative QoL, while considering the individual participants and contexts, may enhance both PA motivation and participants' health and QoL.
Keywords: Motor activity; Participant views; Quality of life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest with the material presented in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Berger BG, Tobar D. Physical activity and quality of life. In: Tenenbaum G, Eklund RC, editors. Handbook of sport psychology. 3rd ed. Hoboken: Wiley; 2007. pp. 598–620.
-
- Gillison FB, Skevington SM, Sato A, Standage M, Evangelidou S. The effects of exercise interventions on quality of life in clinical and healthy populations: a meta-analysis. Soc Sci Med. 2009;68(9):1700–1710. - PubMed
-
- McAuley E, Elavsky S. Physical activity, aging, and quality of life: implications for measurement. In: Zhu W, Chodzko-Zajko W, editors. Measurement issues in aging and physical activity. Champaign: Human Kinetics; 2005. pp. 57–68.
-
- Bize R, Johnson JA, Plotnikoff RC. Physical activity level and health-related quality of life in the general adult population: a systematic review. Prev Med. 2007;45(6):401–415. - PubMed
-
- Gill DL, Williams K, Williams L, Kim BJ, Schultz AM, Araki K, et al. Physical activity behaviors and values of older women [abstract] J Exerc Sport Psychol. 2003;25:S59–S60.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources