Gestational choline supplementation normalized fetal alcohol-induced alterations in histone modifications, DNA methylation, and proopiomelanocortin (POMC) gene expression in β-endorphin-producing POMC neurons of the hypothalamus
- PMID: 23413810
- PMCID: PMC3659188
- DOI: 10.1111/acer.12082
Gestational choline supplementation normalized fetal alcohol-induced alterations in histone modifications, DNA methylation, and proopiomelanocortin (POMC) gene expression in β-endorphin-producing POMC neurons of the hypothalamus
Abstract
Background: Prenatal exposure to ethanol (EtOH) reduces the expression of hypothalamic proopiomelanocortin (POMC) gene, known to control various physiological functions including the organismal stress response. In this study, we determined whether the changes in POMC neuronal functions are associated with altered expressions of histone-modifying and DNA-methylating enzymes in POMC-producing neurons, because these enzymes are known to be involved in regulation of gene expression. In addition, we tested whether gestational choline supplementation prevents the adverse effects of EtOH on these neurons.
Methods: Pregnant rat dams were fed with alcohol-containing liquid diet or control diet during gestational days 7 and 21 with or without choline, and their male offspring rats were used during the adult period. Using double-immunohistochemistry, real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and methylation-specific RT-PCR, we determined protein and mRNA levels of histone-modifying and DNA-methylating enzymes and the changes in POMC gene methylation and expression in the hypothalamus of adult male offspring rats. Additionally, we measured the basal- and lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced corticosterone levels in plasma by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay.
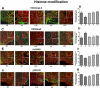
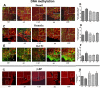
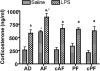
Results: Prenatal EtOH treatment suppressed hypothalamic levels of protein and mRNA of histone activation marks (H3K4me3, Set7/9, acetylated H3K9, phosphorylated H3S10), and increased the repressive marks (H3K9me2, G9a, Setdb1), DNA-methylating enzyme (Dnmt1), and the methyl-CpG-binding protein (MeCP2). The treatment also elevated the level of POMC gene methylation, while it reduced levels of POMC mRNA and β-EP and elevated corticosterone response to LPS. Gestational choline normalized the EtOH-altered protein and the mRNA levels of H3K4me3, Set7/9, H3K9me2, G9a, Setdb1, Dnmt1, and MeCP2. It also normalizes the changes in POMC gene methylation and gene expression, β-EP production, and the corticosterone response to LPS.
Conclusions: These data suggest that prenatal EtOH modulates histone and DNA methylation in POMC neurons that may be resulting in hypermethylation of POMC gene and reduction in POMC gene expression. Gestational choline supplementation prevents the adverse effects of EtOH on these neurons.
Keywords: Choline; DNA Methylation; Fetal Alcohol; Histone Modification; Proopiomelanocortin; Stress Axis.
Copyright © 2013 by the Research Society on Alcoholism.
Figures
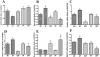
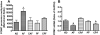
References
-
- Arjona A, Boyadjieva N, Kuhn P, Sarkar DK. Fetal ethanol exposure disrupts the daily rhythms of splenic granzyme B, IFN-gamma, and NK cell cytotoxicity in adulthood. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2006;30:1039–1044. - PubMed
-
- Berman RF, Hannigan JH. Effects of prenatal alcohol exposure on the hippocampus: spatial behavior, electrophysiology and neuroanatomy. Hippocampus. 2000;10:94–110. - PubMed
-
- Boyadjieva NI, Ortigüela M, Arjona A, Cheng X, Sarkar DK. β-endorphin neuronal cell transplant reduces corticotropin releasing hormone hyperresponse to lipopolysaccharide and eliminates natural killer cell functional deficiencies in fetal alcohol exposed rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2009;33:931–937. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

