Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2010
- PMID: 23415502
- PMCID: PMC3810369
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jand.2012.12.016
Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2010
Erratum in
- J Acad Nutr Diet. 2016 Jan;116(1):170
Abstract
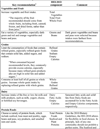
The Healthy Eating Index (HEI) is a measure of diet quality in terms of conformance with federal dietary guidance. Publication of the 2010 Dietary Guidelines for Americans prompted an interagency working group to update the HEI. The HEI-2010 retains several features of the 2005 version: (a) it has 12 components, many unchanged, including nine adequacy and three moderation components; (b) it uses a density approach to set standards, eg, per 1,000 calories or as a percentage of calories; and (c) it employs least-restrictive standards; ie, those that are easiest to achieve among recommendations that vary by energy level, sex, and/or age. Changes to the index include: (a) the Greens and Beans component replaces Dark Green and Orange Vegetables and Legumes; (b) Seafood and Plant Proteins has been added to capture specific choices from the protein group; (c) Fatty Acids, a ratio of polyunsaturated and monounsaturated to saturated fatty acids, replaces Oils and Saturated Fat to acknowledge the recommendation to replace saturated fat with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fatty acids; and (d) a moderation component, Refined Grains, replaces the adequacy component, Total Grains, to assess overconsumption. The HEI-2010 captures the key recommendations of the 2010 Dietary Guidelines and, like earlier versions, will be used to assess the diet quality of the US population and subpopulations, evaluate interventions, research dietary patterns, and evaluate various aspects of the food environment.
Copyright © 2013 Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- US Department of Agriculture and US Department of Health and Human Services. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2010. 7th ed. Washington, DC: 2010. http://www.cnpp.usda.gov/dietaryguidelines.htm. - PubMed
-
- Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM. A comparison of food-based recommendations and nutrient values of three food guides: USDA's MyPyramid, NHLBI's Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension Eating Plan, and Harvard's Healthy Eating Pyramid. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108(3):522–528. - PubMed
-
- Guenther PM, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM. Development of the Healthy Eating Index-2005. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108(11):1896–1901. - PubMed
-
- Guenther PM, Reedy J, Krebs-Smith SM, Reeve BB. Evaluation of the Healthy Eating Index-2005. J Am Diet Assoc. 2008;108(11):1854–1864. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Department of Agriculture Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion. [Accessed September 29, 2011];What Are Empty Calories? http://www.choosemyplate.gov/weight-management-calories/calories/empty-c....
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

