ADAMTS7 cleavage and vascular smooth muscle cell migration is affected by a coronary-artery-disease-associated variant
- PMID: 23415669
- PMCID: PMC3591856
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.01.012
ADAMTS7 cleavage and vascular smooth muscle cell migration is affected by a coronary-artery-disease-associated variant
Abstract
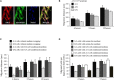
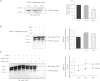
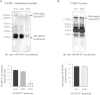
Recent genome-wide association studies have revealed an association between variation at the ADAMTS7 locus and susceptibility to coronary artery disease (CAD). Furthermore, in a population-based study cohort, we observed an inverse association between atherosclerosis prevalence and rs3825807, a nonsynonymous SNP (A to G) leading to a Ser-to-Pro substitution in the prodomain of the protease ADAMTS7. In light of these data, we sought a mechanistic explanation for this association. We found that ADAMTS7 accumulated in smooth muscle cells in coronary and carotid atherosclerotic plaques. Vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) of the G/G genotype for rs3825807 had reduced migratory ability, and conditioned media of VSMCs of the G/G genotype contained less of the cleaved form of thrombospondin-5, an ADAMTS7 substrate that had been shown to be produced by VSMCs and inhibit VSMC migration. Furthermore, we found that there was a reduction in the amount of cleaved ADAMTS7 prodomain in media conditioned by VSMCs of the G/G genotype and that the Ser-to-Pro substitution affected ADAMTS7 prodomain cleavage. The results of our study indicate that rs3825807 has an effect on ADAMTS7 maturation, thrombospondin-5 cleavage, and VSMC migration, with the variant associated with protection from atherosclerosis and CAD rendering a reduction in ADAMTS7 function.
Copyright © 2013 The American Society of Human Genetics. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Schunkert H., König I.R., Kathiresan S., Reilly M.P., Assimes T.L., Holm H., Preuss M., Stewart A.F., Barbalic M., Gieger C., Cardiogenics. CARDIoGRAM Consortium Large-scale association analysis identifies 13 new susceptibility loci for coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:333–338. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reilly M.P., Li M., He J., Ferguson J.F., Stylianou I.M., Mehta N.N., Burnett M.S., Devaney J.M., Knouff C.W., Thompson J.R., Myocardial Infarction Genetics Consortium. Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium Identification of ADAMTS7 as a novel locus for coronary atherosclerosis and association of ABO with myocardial infarction in the presence of coronary atherosclerosis: two genome-wide association studies. Lancet. 2011;377:383–392. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Coronary Artery Disease (C4D) Genetics Consortium A genome-wide association study in Europeans and South Asians identifies five new loci for coronary artery disease. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:339–344. - PubMed
-
- Somerville R.P., Longpré J.M., Apel E.D., Lewis R.M., Wang L.W., Sanes J.R., Leduc R., Apte S.S. ADAMTS7B, the full-length product of the ADAMTS7 gene, is a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan containing a mucin domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:35159–35175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

