The multiple roles for Sox2 in stem cell maintenance and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 23416461
- PMCID: PMC3871517
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.02.013
The multiple roles for Sox2 in stem cell maintenance and tumorigenesis
Abstract
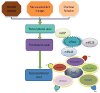
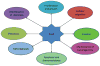
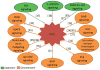
The Sry-containing protein Sox2 initially was known to regulate the self-renewal of the mouse and human embryonic stem cells (ESCs). It is also important for the maintenance of stem cells in multiple adult tissues including the brain and trachea, and it is one of the key transcription factors for establishing induced pluripotent stem cells. Recently, overexpression and gene amplification of Sox2 have been associated with the development of squamous cell carcinoma in multiple tissues such as the lung and esophagus. These different roles for Sox2 involve a complicated regulatory networks consisting of microRNAs, kinases and signaling molecules. While the levels of Sox2 are modulated transcriptionally and translationally, post-translational modification is also important for the various functions of Sox2. In clinics, high levels of Sox2 are correlated with poor prognosis and increased proliferation of cancer stem cells. Therefore targeting Sox2 can be potentially explored for a new therapeutic avenue to treat cancers. This review will focus on the different roles for Sox2 in stem cell maintenance and its oncogenic roles in the context of signal transcription and microRNA regulation. We will also review the main upstream and downstream targets of Sox2, which can be potentially used as therapeutic measures to treat cancer with abnormal levels of Sox2.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Xu N, Papagiannakopoulos T, Pan G, Thomson JA, Kosik KS. MicroRNA-145 regulates OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 and represses pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2009;137:647–58. - PubMed
-
- Jeon HM, Sohn YW, Oh SY, Kim SH, Beck S, Kim S, et al. ID4 imparts chemoresistance and cancer stemness to glioma cells by derepressing miR-9*-mediated suppression of SOX2. Cancer Res. 2011;71:3410–21. - PubMed
-
- Liu T, Cheng W, Huang Y, Huang Q, Jiang L, Guo L. Human amniotic epithelial cell feeder layers maintain human iPS cell pluripotency via inhibited endogenous microRNA-145 and increased Sox2 expression. Exp Cell Res. 2012;318:424–34. - PubMed
-
- Tsuruzoe S, Ishihara K, Uchimura Y, Watanabe S, Sekita Y, Aoto T, et al. Inhibition of DNA binding of Sox2 by the SUMO conjugation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351:920–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

