Compartmentalization of metabolic pathways in yeast mitochondria improves the production of branched-chain alcohols
- PMID: 23417095
- PMCID: PMC3659820
- DOI: 10.1038/nbt.2509
Compartmentalization of metabolic pathways in yeast mitochondria improves the production of branched-chain alcohols
Abstract
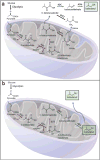
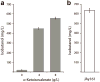
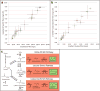
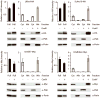
Efforts to improve the production of a compound of interest in Saccharomyces cerevisiae have mainly involved engineering or overexpression of cytoplasmic enzymes. We show that targeting metabolic pathways to mitochondria can increase production compared with overexpression of the enzymes involved in the same pathways in the cytoplasm. Compartmentalization of the Ehrlich pathway into mitochondria increased isobutanol production by 260%, whereas overexpression of the same pathway in the cytoplasm only improved yields by 10%, compared with a strain overproducing enzymes involved in only the first three steps of the biosynthetic pathway. Subcellular fractionation of engineered strains revealed that targeting the enzymes of the Ehrlich pathway to the mitochondria achieves greater local enzyme concentrations. Other benefits of compartmentalization may include increased availability of intermediates, removing the need to transport intermediates out of the mitochondrion and reducing the loss of intermediates to competing pathways.
Figures

Comment in
-
Compartmentalizing metabolic pathways in organelles.Nat Biotechnol. 2013 Apr;31(4):320-1. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2549. Nat Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23563429 No abstract available.
References
-
- Attardi G, Schatz G. Biogenesis of mitochondria. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:289–333. - PubMed
-
- Fukuda H, Casas A, Batlle A. Aminolevulinic acid: from its unique biological function to its star role in photodynamic therapy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37:272–276. - PubMed
-
- Lange H, Kispal G, Lill R. Mechanism of iron transport to the site of heme synthesis inside yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:18989–18996. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

