The nonconventional MHC class II molecule DM governs diabetes susceptibility in NOD mice
- PMID: 23418596
- PMCID: PMC3572069
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056738
The nonconventional MHC class II molecule DM governs diabetes susceptibility in NOD mice
Abstract
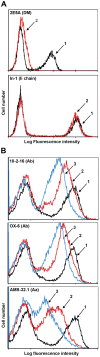
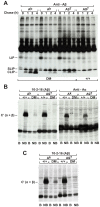
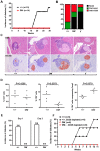
The spontaneous destruction of insulin producing pancreatic beta cells in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice provides a valuable model of type 1 diabetes. As in humans, disease susceptibility is controlled by the classical MHC class II genes that guide CD4(+) T cell responses to self and foreign antigens. It has long been suspected that the dedicated class II chaperone designated HLA-DM in humans or H-2M in mice also makes an important contribution, but due to tight linkage within the MHC, a possible role played by DM peptide editing has not been previously tested by conventional genetic approaches. Here we exploited newly established germ-line competent NOD ES cells to engineer a loss of function allele. DM deficient NOD mice display defective class II peptide occupancy and surface expression, and are completely protected against type 1 diabetes. Interestingly the mutation results in increased proportional representation of CD4(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells and the absence of pathogenic CD4(+) T effectors. Overall, this striking phenotype establishes that DM-mediated peptide selection plays an essential role in the development of autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Todd JA, Bell JI, McDevitt HO (1987) HLA-DQbeta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature 329: 599–604. - PubMed
-
- Serreze DV, Leiter EH (2001) Genes and cellular requirements for autoimmune diabetes susceptibility in nonobese diabetic mice. Curr Dir Autoimmun 4: 31–67. - PubMed
-
- Todd JA, Wicker LS (2001) Genetic protection from the inflammatory disease type diabetes in humans and animal models. Immunity 15: 387–395. - PubMed
-
- Corper AL, Stratmann T, Apostolopoulos V, Scott CA, Garcia KC, et al. (2000) A structural framework for deciphering the link between I-Ag7 and autoimmune diabetes. Science 288: 505–511. - PubMed
-
- Latek RR, Suri A, Petzold SJ, Nelson CA, Kanagawa O, et al. (2000) Structural basis of peptide binding and presentation by the type 1 diabetes-associated MHC class II molecule of NOD mice. Immunity 12: 699–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

