Energy metabolism and energy-sensing pathways in mammalian embryonic and adult stem cell fate
- PMID: 23420198
- PMCID: PMC3575699
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.114827
Energy metabolism and energy-sensing pathways in mammalian embryonic and adult stem cell fate
Abstract
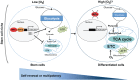
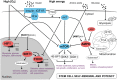
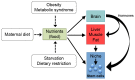
Metabolism is influenced by age, food intake, and conditions such as diabetes and obesity. How do physiological or pathological metabolic changes influence stem cells, which are crucial for tissue homeostasis? This Commentary reviews recent evidence that stem cells have different metabolic demands than differentiated cells, and that the molecular mechanisms that control stem cell self-renewal and differentiation are functionally connected to the metabolic state of the cell and the surrounding stem cell niche. Furthermore, we present how energy-sensing signaling molecules and metabolism regulators are implicated in the regulation of stem cell self-renewal and differentiation. Finally, we discuss the emerging literature on the metabolism of induced pluripotent stem cells and how manipulating metabolic pathways might aid cellular reprogramming. Determining how energy metabolism regulates stem cell fate should shed light on the decline in tissue regeneration that occurs during aging and facilitate the development of therapies for degenerative or metabolic diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Banko M. R., Allen J. J., Schaffer B. E., Wilker E. W., Tsou P., White J. L., Villén J., Wang B., Kim S. R., Sakamoto K.et al. (2011). Chemical genetic screen for AMPKα2 substrates uncovers a network of proteins involved in mitosis. Mol. Cell 44, 878–892 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.11.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bonnert T. P., Bilsland J. G., Guest P. C., Heavens R., McLaren D., Dale C., Thakur M., McAllister G., Munoz–Sanjuan I. (2006). Molecular characterization of adult mouse subventricular zone progenitor cells during the onset of differentiation. Eur. J. Neurosci. 24, 661–675 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.04912.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

