Innate lymphoid type 2 cells sustain visceral adipose tissue eosinophils and alternatively activated macrophages
- PMID: 23420878
- PMCID: PMC3600903
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20121964
Innate lymphoid type 2 cells sustain visceral adipose tissue eosinophils and alternatively activated macrophages
Abstract
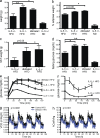
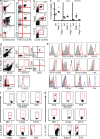
Eosinophils in visceral adipose tissue (VAT) have been implicated in metabolic homeostasis and the maintenance of alternatively activated macrophages (AAMs). The absence of eosinophils can lead to adiposity and systemic insulin resistance in experimental animals, but what maintains eosinophils in adipose tissue is unknown. We show that interleukin-5 (IL-5) deficiency profoundly impairs VAT eosinophil accumulation and results in increased adiposity and insulin resistance when animals are placed on a high-fat diet. Innate lymphoid type 2 cells (ILC2s) are resident in VAT and are the major source of IL-5 and IL-13, which promote the accumulation of eosinophils and AAM. Deletion of ILC2s causes significant reductions in VAT eosinophils and AAMs, and also impairs the expansion of VAT eosinophils after infection with Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, an intestinal parasite associated with increased adipose ILC2 cytokine production and enhanced insulin sensitivity. Further, IL-33, a cytokine previously shown to promote cytokine production by ILC2s, leads to rapid ILC2-dependent increases in VAT eosinophils and AAMs. Thus, ILC2s are resident in VAT and promote eosinophils and AAM implicated in metabolic homeostasis, and this axis is enhanced during Th2-associated immune stimulation.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 AI078869/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063720/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- AI026918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007618/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL107202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI026918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AI095319/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- T32 AI007641/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HD044331/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK094641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI026918/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI030663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI030663/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076746/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AI078869/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HL107202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

