Annealing effect on Sb2S3-TiO2 nanostructures for solar cell applications
- PMID: 23421351
- PMCID: PMC3598216
- DOI: 10.1186/1556-276X-8-89
Annealing effect on Sb2S3-TiO2 nanostructures for solar cell applications
Abstract
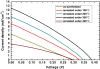
Nanostructures composited of vertical rutile TiO2 nanorod arrays and Sb2S3 nanoparticles were prepared on an F:SnO2 conductive glass by hydrothermal method and successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction method at low temperature. Sb2S3-sensitized TiO2 nanorod solar cells were assembled using the Sb2S3-TiO2 nanostructure as the photoanode and a polysulfide solution as an electrolyte. Annealing effects on the optical and photovoltaic properties of Sb2S3-TiO2 nanostructure were studied systematically. As the annealing temperatures increased, a regular red shift of the bandgap of Sb2S3 nanoparticles was observed, where the bandgap decreased from 2.25 to 1.73 eV. At the same time, the photovoltaic conversion efficiency for the nanostructured solar cells increased from 0.46% up to 1.47% as a consequence of the annealing effect. This improvement can be explained by considering the changes in the morphology, the crystalline quality, and the optical properties caused by the annealing treatment.
Figures
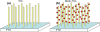



References
-
- O'Regan B, Grätzel M. A low-cost, high-efficiency solar-cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature. 1991;353:737. doi: 10.1038/353737a0. - DOI
-
- Hossain MF, Zhang ZH, Takahashi T. Novel micro-ring structured ZnO photoelectrode for dye-sensitized solar cell. Nano-Micro Lett. 2010;2:53.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

