Inflammatory networks and immune surveillance of pancreatic carcinoma
- PMID: 23422836
- PMCID: PMC3647365
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.01.006
Inflammatory networks and immune surveillance of pancreatic carcinoma
Abstract
Cancer-associated inflammation plays an important role in restraining anti-tumor immunity, particularly in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDA) for which a massive infiltration of immunosuppressive leukocytes into the tumor stroma is an early and consistent event in oncogenesis. Intratumoral effector T cells are rare. This pathophysiology is in contrast to many other solid tumors for which infiltration of effector T cells is often prominent, associated with improved clinical outcomes, and mechanistically contributes to tumor immunoediting that ultimately can mediate immune escape. In PDA, increasing evidence suggests that the ras oncogene drives an inflammatory program that establishes immune privilege in the tumor microenvironment. Indeed, PDA cells might remain intrinsically sensitive to T cell killing because they have never been exposed to T cell selective pressure in vivo. In support of this hypothesis, recent studies demonstrate that derailing immune suppressive pathways in the PDA microenvironment, such as tumor derived GM-CSF, facilitates T-cell mediated tumor rejection. These findings carry major implications for the development of novel, combination immunotherapies for pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
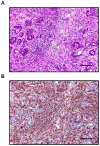
References
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–674. - PubMed
-
- Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity’s roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. 2011;331:1565–1570. Outstanding analysis of the prevailing “triple E” hypothesis of cancer immunosurveillance. - PubMed
-
- Dunn GP, Old LJ, Schreiber RD. The three Es of cancer immunoediting. Annu Rev Immunol. 2004;22:329–360. - PubMed
-
- Zhang B, Kracker S, Yasuda T, Casola S, Vanneman M, Homig-Holzel C, Wang Z, Derudder E, Li S, Chakraborty T, et al. Immune surveillance and therapy of lymphomas driven by Epstein-Barr virus protein LMP1 in a mouse model. Cell. 2012;148:739–751. T cells function as potent extrinic immune suppressors in hematological malignancies. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

