HAMP domain conformers that propagate opposite signals in bacterial chemoreceptors
- PMID: 23424282
- PMCID: PMC3570549
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001479
HAMP domain conformers that propagate opposite signals in bacterial chemoreceptors
Abstract
HAMP domains are signal relay modules in >26,000 receptors of bacteria, eukaryotes, and archaea that mediate processes involved in chemotaxis, pathogenesis, and biofilm formation. We identify two HAMP conformations distinguished by a four- to two-helix packing transition at the C-termini that send opposing signals in bacterial chemoreceptors. Crystal structures of signal-locked mutants establish the observed structure-to-function relationships. Pulsed dipolar electron spin resonance spectroscopy of spin-labeled soluble receptors active in cells verify that the crystallographically defined HAMP conformers are maintained in the receptors and influence the structure and activity of downstream domains accordingly. Mutation of HR2, a key residue for setting the HAMP conformation and generating an inhibitory signal, shifts HAMP structure and receptor output to an activating state. Another HR2 variant displays an inverted response with respect to ligand and demonstrates the fine energetic balance between "on" and "off" conformers. A DExG motif found in membrane proximal HAMP domains is shown to be critical for responses to extracellular ligand. Our findings directly correlate in vivo signaling with HAMP structure, stability, and dynamics to establish a comprehensive model for HAMP-mediated signal relay that consolidates existing views on how conformational signals propagate in receptors. Moreover, we have developed a rational means to manipulate HAMP structure and function that may prove useful in the engineering of bacterial taxis responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
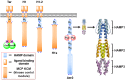
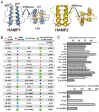
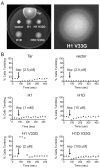
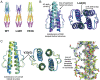
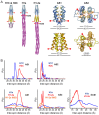
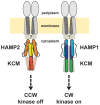
Comment in
-
A little switch: alternative domain conformations control bacterial flagella rotation direction.PLoS Biol. 2013;11(2):e1001480. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1001480. Epub 2013 Feb 12. PLoS Biol. 2013. PMID: 23424283 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Parkinson JS (2010) Signaling mechanisms of HAMP domains in chemoreceptors and sensor kinases. Annu Rev Microbiol 64: 101–122. - PubMed
-
- Hulko M, Berndt F, Gruber M, Linder JU, Truffault V, et al. (2006) The HAMP domain structure implies helix rotation in transmembrane signaling. Cell 126: 929–940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

