(7aR)-1-[(2R,5S,E)-6-Hy-droxy-5,6-dimethyl-hept-3-en-2-yl]-7a-methyl-hexa-hydro-1H-inden-4(2H)-one
- PMID: 23424499
- PMCID: PMC3569753
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536812051343
(7aR)-1-[(2R,5S,E)-6-Hy-droxy-5,6-dimethyl-hept-3-en-2-yl]-7a-methyl-hexa-hydro-1H-inden-4(2H)-one
Abstract
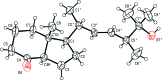
The chiral title compound, C(19)H(32)O(2), contains a [4.3.0]-bicyclic moiety in which the shared C-C bond presents a trans configuration and a side chain in which the C=C double bond shows an E conformation. The conformations of five- and six-membered rings are envelope (with the bridgehead atom bearing the methyl substituent as the flap) and chair, respectively, with a dihedral angle of 4.08 (17)° between the idealized planes of the rings. In the crystal, the mol-ecules are self-assembled via classical O-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming chains along [112]; these chains are linked by weak non-classical C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds, giving a two-dimensional supra-molecular structure parallel to (010). The absolute configuration was established according to the configuration of the starting material.
Figures

References
-
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madinson, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cremer, D. & Pople, J. A. (1975). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 97, 1354–1358.
-
- Henry, H. L. (2011). Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 25, 531–541. - PubMed
-
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
