(S)-2,2'-Dihy-droxy-N,N'-(6-hy-droxy-hexane-1,5-di-yl)dibenzamide
- PMID: 23424504
- PMCID: PMC3569758
- DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813000354
(S)-2,2'-Dihy-droxy-N,N'-(6-hy-droxy-hexane-1,5-di-yl)dibenzamide
Abstract
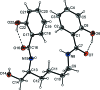
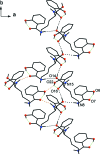
In the title compound, C(20)H(24)N(2)O(5), the dihedral angle between the two roughly planar salicyl-amide fragments [r.m.s. deviations = 0.043 (2) and 0.149 (2) Å] is 25.50 (5)°. The mol-ecular conformation is stabilized by intra-molecular O-H⋯O hydrogen bonds involving phenol -OH groups and amide O atoms. Inter-molecular hy-droxy-meth-yl-amide O-H⋯O and amine-hy-droxy-methyl N-H⋯O hydrogen bonds form infinite chains along the b axis. These chains are further inter-linked by amine-amide N-H⋯O and phenol-phenol O-H⋯O inter-actions, thus giving layers parallel to (001).
Figures
References
-
- Brandenburg, K. (2012). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
-
- Bruker (2010). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Cappillino, P. J., Tarves, P. C., Rowe, G. T., Lewis, A. J., Harvey, M., Rogge, C., Stassinopoulos, A., Lo, W., Armstrong, W. H. & Caradonna, J. P. (2009). Inorg. Chim. Acta, 362, 2136–2150.
-
- Duhme, A.-K., Dauter, Z., Hider, R. C. & Pohl, S. (1996). Inorg. Chem. 35, 3059–3061.
-
- Huang, S.-P., Franz, K. J., Olmstead, M. M. & Fish, R. H. (1995). Inorg. Chem. 34, 2820–2825.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
