Functional organization of human sensorimotor cortex for speech articulation
- PMID: 23426266
- PMCID: PMC3606666
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11911
Functional organization of human sensorimotor cortex for speech articulation
Erratum in
- Nature. 2013 Jun 27;498(7455):526
Abstract
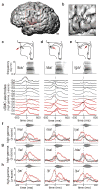
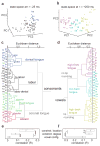
Speaking is one of the most complex actions that we perform, but nearly all of us learn to do it effortlessly. Production of fluent speech requires the precise, coordinated movement of multiple articulators (for example, the lips, jaw, tongue and larynx) over rapid time scales. Here we used high-resolution, multi-electrode cortical recordings during the production of consonant-vowel syllables to determine the organization of speech sensorimotor cortex in humans. We found speech-articulator representations that are arranged somatotopically on ventral pre- and post-central gyri, and that partially overlap at individual electrodes. These representations were coordinated temporally as sequences during syllable production. Spatial patterns of cortical activity showed an emergent, population-level representation, which was organized by phonetic features. Over tens of milliseconds, the spatial patterns transitioned between distinct representations for different consonants and vowels. These results reveal the dynamic organization of speech sensorimotor cortex during the generation of multi-articulator movements that underlies our ability to speak.
Figures


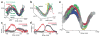
References
-
- Levelt WJM. Speaking: From Intention to Articulation. MIT Press; 1993.
-
- Ladefoged P, Johnson K. A Course in Phonetics. Wadsworth Publishing; 2010.
-
- Browman CP, Goldstein L. Articulatory Gestures as Phonological Units. Haskins Laboratories Status Report on Speech Research. 1989;99:69–101.
-
- Fowler CA, Rubin PE, Remez RE, Turvey MT. Language Production. In: Butterworth B, editor. Speech and Talk. Vol. 1. Academic Press; 1980. pp. 373–420.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

