Bacteria penetrate the normally impenetrable inner colon mucus layer in both murine colitis models and patients with ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 23426893
- PMCID: PMC3740207
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303207
Bacteria penetrate the normally impenetrable inner colon mucus layer in both murine colitis models and patients with ulcerative colitis
Abstract
Objective: The inner mucus layer in mouse colon normally separates bacteria from the epithelium. Do humans have a similar inner mucus layer and are defects in this mucus layer a common denominator for spontaneous colitis in mice models and ulcerative colitis (UC)?
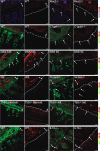
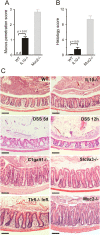
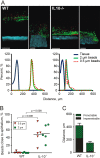
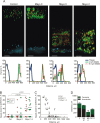
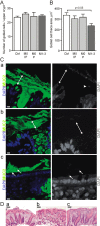
Methods and results: The colon mucus layer from mice deficient in Muc2 mucin, Core 1 O-glycans, Tlr5, interleukin 10 (IL-10) and Slc9a3 (Nhe3) together with that from dextran sodium sulfate-treated mice was immunostained for Muc2, and bacterial localisation in the mucus was analysed. All murine colitis models revealed bacteria in contact with the epithelium. Additional analysis of the less inflamed IL-10(-/-) mice revealed a thicker mucus layer than wild-type, but the properties were different, as the inner mucus layer could be penetrated both by bacteria in vivo and by fluorescent beads the size of bacteria ex vivo. Clear separation between bacteria or fluorescent beads and the epithelium mediated by the inner mucus layer was also evident in normal human sigmoid colon biopsy samples. In contrast, mucus on colon biopsy specimens from patients with UC with acute inflammation was highly penetrable. Most patients with UC in remission had an impenetrable mucus layer similar to that of controls.
Conclusions: Normal human sigmoid colon has an inner mucus layer that is impenetrable to bacteria. The colon mucus in animal models that spontaneously develop colitis and in patients with active UC allows bacteria to penetrate and reach the epithelium. Thus colon mucus properties can be modulated, and this suggests a novel model of UC pathophysiology.
Keywords: BACTERIAL TRANSLOCATION; MUCINS; MUCOSAL BARRIER; MUCOSAL PATHOLOGY; MUCUS.
Figures
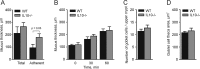
References
-
- Xavier RJ, Podolsky DK. Unravelling the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature 2007;448:427–34 - PubMed
-
- Sartor RB. Therapeutic manipulation of the enteric microflora in inflammatory bowel diseases: antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics. Gastroenterology 2004;126:1620–33 - PubMed
-
- Danese S, Fiocchi C. Ulcerative Colitis. New Engl J Med 2011;365:1713–25 - PubMed
-
- Schirbel A, Fiocchi C. Inflammatory bowel disease: established and evolving considerations on its etiopathogenesis and therapy. J Dig Dis 2010;11:266–76 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
