Cross-hemispheric functional connectivity in the human fetal brain
- PMID: 23427244
- PMCID: PMC3618956
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3004978
Cross-hemispheric functional connectivity in the human fetal brain
Abstract
Compelling evidence indicates that psychiatric and developmental disorders are generally caused by disruptions in the functional connectivity (FC) of brain networks. Events occurring during development, and in particular during fetal life, have been implicated in the genesis of such disorders. However, the developmental timetable for the emergence of neural FC during human fetal life is unknown. We present the results of resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging performed in 25 healthy human fetuses in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy (24 to 38 weeks of gestation). We report the presence of bilateral fetal brain FC and regional and age-related variation in FC. Significant bilateral connectivity was evident in half of the 42 areas tested, and the strength of FC between homologous cortical brain regions increased with advancing gestational age. We also observed medial to lateral gradients in fetal functional brain connectivity. These findings improve understanding of human fetal central nervous system development and provide a basis for examining the role of insults during fetal life in the subsequent development of disorders in neural FC.
Figures
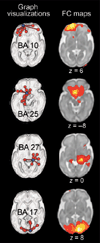



References
-
- Cao Q, Zang Y, Sun L, Sui M, Long X, Zou Q, Wang Y. Abnormal neural activity in children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuroreport. 2006;17:1033–1036. - PubMed
-
- Tian L, Jiang T, Wang Y, Zang Y, He Y, Liang M, Sui M, Cao Q, Hu S, Peng M, Zhuo Y. Altered resting-state functional connectivity patterns of anterior cingulate cortex in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2006;400:39–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

