Safety and efficacy of an injectable extracellular matrix hydrogel for treating myocardial infarction
- PMID: 23427245
- PMCID: PMC3848875
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3005503
Safety and efficacy of an injectable extracellular matrix hydrogel for treating myocardial infarction
Erratum in
- Sci Transl Med. 2014 Apr 23;6(233):233er2
Abstract
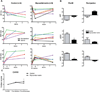
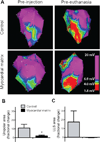
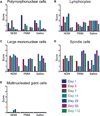
New therapies are needed to prevent heart failure after myocardial infarction (MI). As experimental treatment strategies for MI approach translation, safety and efficacy must be established in relevant animal models that mimic the clinical situation. We have developed an injectable hydrogel derived from porcine myocardial extracellular matrix as a scaffold for cardiac repair after MI. We establish the safety and efficacy of this injectable biomaterial in large- and small-animal studies that simulate the clinical setting. Infarcted pigs were treated with percutaneous transendocardial injections of the myocardial matrix hydrogel 2 weeks after MI and evaluated after 3 months. Echocardiography indicated improvement in cardiac function, ventricular volumes, and global wall motion scores. Furthermore, a significantly larger zone of cardiac muscle was found at the endocardium in matrix-injected pigs compared to controls. In rats, we establish the safety of this biomaterial and explore the host response via direct injection into the left ventricular lumen and in an inflammation study, both of which support the biocompatibility of this material. Hemocompatibility studies with human blood indicate that exposure to the material at relevant concentrations does not affect clotting times or platelet activation. This work therefore provides a strong platform to move forward in clinical studies with this cardiac-specific biomaterial that can be delivered by catheter.
Figures



References
-
- Christman KL, Lee RJ. Biomaterials for the treatment of myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006 Sep 5;48:907. - PubMed
-
- Rane AA, Christman KL. Biomaterials for the treatment of myocardial infarction a 5-year update. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2011 Dec 13;58:2615. - PubMed
-
- Johnson TD, Christman KL. Injectable hydrogel therapies and their delivery strategies for treating myocardial infarction. Expert opinion on drug delivery. 2012 Nov 9; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

