Immunosuppression in sepsis: a novel understanding of the disorder and a new therapeutic approach
- PMID: 23427891
- PMCID: PMC3798159
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70001-X
Immunosuppression in sepsis: a novel understanding of the disorder and a new therapeutic approach
Abstract
Failures of highly touted trials have caused experts to call for re-evaluation of the current approach toward sepsis. New research has revealed key pathogenic mechanisms; autopsy results have shown that most patients admitted to intensive care units for treatment of sepsis had unresolved septic foci at post mortem, suggesting that patients were unable to eradicate invading pathogens and were more susceptible to nosocomial organisms, or both. These results suggest that therapies that improve host immunity might increase survival. Additional work showed that cytokine production by splenocytes taken post mortem from patients who died of sepsis is profoundly suppressed, possibly because of so-called T-cell exhaustion-a newly recognised immunosuppressive mechanism that occurs with chronic antigenic stimulation. Results from two clinical trials of biomarker-guided therapeutic drugs that boosted immunity showed promising findings in sepsis. Collectively, these studies emphasise the degree of immunosuppression that occurs in sepsis, and explain why many previous sepsis trials which were directed at blocking inflammatory mediators or pathogen recognition signalling pathways failed. Finally, highly encouraging results from use of the new immunomodulatory molecules interleukin 7 and anti-programmed cell death 1 in infectious disease point the way for possible use in sepsis. We hypothesise that immunoadjuvant therapy represents the next major advance in sepsis.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
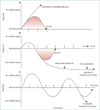
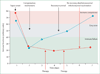

Comment in
-
Adjunctive treatment of severe sepsis.Lancet Infect Dis. 2013 Nov;13(11):917-8. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(13)70289-5. Lancet Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 24156894 No abstract available.
References
-
- Cohen J, Opal S, Calandra T. Sepsis studies need new direction. Lancet Infect Dis. 2012;12:503–505. - PubMed
-
- Wenzel RP, Edmond MB. Septic shock: evaluating another failed treatment. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2122–2124. - PubMed
-
- Williams SC. After Xigris, researchers look to new targets to combat sepsis. Nat Med. 2012;18:1001. - PubMed
-
- Dolgin E. Trial failure prompts soul-searching for critical-care specialists. Nat Med. 2012;18:1000. - PubMed
-
- Angus DC. The search for effective therapy for sepsis: back to the drawing board? JAMA. 2011;306:2614–2615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

