Supplemental vitamin D and physical performance in COPD: a pilot randomized trial
- PMID: 23430315
- PMCID: PMC3575124
- DOI: 10.2147/COPD.S40885
Supplemental vitamin D and physical performance in COPD: a pilot randomized trial
Abstract
Background: Low 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels, commonly observed in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are associated with muscle weakness in elderly populations, and vitamin D supplementation appears to improve muscle strength and decrease falls in older individuals. We tested the effect of vitamin D supplementation on physical performance in patients with COPD.
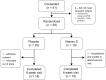
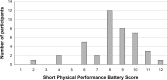
Methods: Patients were randomized to daily cholecalciferol (2000 IU) or placebo for 6 weeks. The primary outcome was the 6-week change in Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) score. Secondary outcomes included changes in the St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) score, and serum 25(OH)D.
Results: Thirty-six participants (mean age 68 years, all Caucasian males, mean forced expiratory volume in one second 33% of predicted) completed the study. Despite an increase in 25(OH)D levels in the intervention arm to a mean of 32.6 ng/mL (versus 22.1 ng/mL in the placebo arm), there was no difference in improvements in either SPPB scores (0.3 point difference; 95% confidence interval -0.8 to 1.5; P = 0.56) or SGRQ scores (2.3 point difference; 95% confidence interval -2.3 to 6.9; P = 0.32).
Conclusion: Among patients with severe COPD, 2000 IU of daily vitamin D for 6 weeks increased 25(OH)D to a level widely considered as normal. However, compared with placebo, short-term vitamin D supplementation had no discernible effect on a simple measure of physical performance.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; randomized controlled trial; skeletal muscle strength; vitamin D.
Figures
References
-
- Decramer M, Gosselink R, Troosters T, Verschueren M, Evers G. Muscle weakness is related to utilization of health care resources in COPD patients. Eur Respir J. 1997;10:417–423. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Dietrich T, Orav EJ, et al. Higher 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations are associated with better lower-extremity function in both active and inactive persons aged ≥ 60 y. Am J Clin Nutr. 2004;80:752–758. - PubMed
-
- Wicherts IS, van Schoor NM, Boeke AJ, et al. Vitamin D status predicts physical performance and its decline in older persons. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:2058–2065. - PubMed
-
- Pfeifer M, Begerow B, Minne HW. Vitamin D and muscle function. Osteoporos Int. 2002;13:187–194. - PubMed
-
- Bischoff-Ferrari HA, Borchers M, Gudat F, Durmuller U, Stahelin HB, Dick W. Vitamin D receptor expression in human muscle tissue decreases with age. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19:265–269. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical