Precise maps of RNA polymerase reveal how promoters direct initiation and pausing
- PMID: 23430654
- PMCID: PMC3974810
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1229386
Precise maps of RNA polymerase reveal how promoters direct initiation and pausing
Abstract
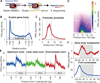
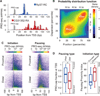
Transcription regulation occurs frequently through promoter-associated pausing of RNA polymerase II (Pol II). We developed a precision nuclear run-on and sequencing (PRO-seq) assay to map the genome-wide distribution of transcriptionally engaged Pol II at base pair resolution. Pol II accumulates immediately downstream of promoters, at intron-exon junctions that are efficiently used for splicing, and over 3' polyadenylation sites. Focused analyses of promoters reveal that pausing is not fixed relative to initiation sites, nor is it specified directly by the position of a particular core promoter element or the first nucleosome. Core promoter elements function beyond initiation, and when optimally positioned they act collectively to dictate the position and strength of pausing. This "complex interaction" model was tested with insertional mutagenesis of the Drosophila Hsp70 core promoter.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

