Simple, Fast, and Simultaneous Detection of Plasma Total Homocysteine, Methylmalonic Acid, Methionine, and 2-Methylcitric Acid Using Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
- PMID: 23430805
- PMCID: PMC3755585
- DOI: 10.1007/8904_2012_205
Simple, Fast, and Simultaneous Detection of Plasma Total Homocysteine, Methylmalonic Acid, Methionine, and 2-Methylcitric Acid Using Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry (LC/MS/MS)
Abstract
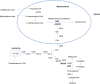
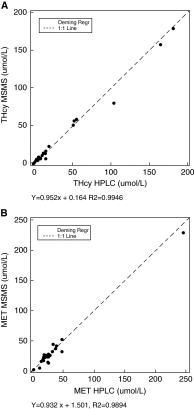
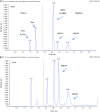
Cobalamin (Vitamin B12) plays an essential role both in the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA and in the synthesis of methionine (Met) from homocysteine (Hcy). Elevations of total homocysteine (tHcy), Met, methylmalonic acid (MMA), and 2-methylcitric acid (2MCA) are indicative of disorders in these related pathways, and can clinically present as methylmalonic acidemia, cobalamin defects or deficiency, propionic acidemia, homocystinuria, and hypermethioninemia. We have developed a fast, sensitive, and simple method for the simultaneous detection of plasma tHcy, MMA, Met, and 2MCA using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS). All analytes were directly determined without the need of derivatization. Both positive and negative modes were used to achieve the best sensitivity and specificity. The two stereo isomers of 2MCA (2S, 3S) and (2R, 3S) were successfully separated and were designated as 2MCA1 and 2MCA2. The assays were linear up to a concentration of 800 μMol/l for tHcy, 2,000 μMol/l for Met, 80 μMol/l for MMA, 40 μMol/l for 2MCA1, and 40 μMol/l for 2MCA2 (80 μMol/l for total 2MCA), respectively. The recovery was between 84.42 % and 120.05 %. The intra-assay coefficient of variations (CVs) ranged from 2.1 % to 6.9 % (n = 20), and the inter-assay CVs ranged from 2.7 % to 11.6 % (n = 20). Reference intervals were established and verified (n = 125). A total of 15 patients with variable disorders in related pathway were successfully confirmed. The assay can be performed either in diagnostic laboratories or as second-tier, follow-up test in newborn screening laboratories.A fast, sensitive, and simple LC/MS/MS method was developed successfully for the simultaneous detection of plasma total homocysteine, methylmalonic acid, methionine, and 2-methylcitric acid for diagnosis of disorders in related pathways.
Figures


References
-
- Campbell CD. Two newborns with nutritional vitamin B12 deficiency: challenges in newborn screening for vitamin B12 deficiency. Heamatologica. 2005;90(12):e119–e121. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

