The management of pregnancy in maple syrup urine disease: experience with two patients
- PMID: 23430812
- PMCID: PMC3755568
- DOI: 10.1007/8904_2013_212
The management of pregnancy in maple syrup urine disease: experience with two patients
Abstract
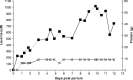
We describe the management and outcomes of pregnancy in two women affected with Maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Both patients had classical disease diagnosed in the newborn period and were managed with low-protein diets and supplements, although compliance was moderately poor throughout life. Both pregnancies were complicated by poor compliance and one patient had a metabolic decompensation, which included seizures and profound encephalopathy, at the end of the first trimester. Peri-partum management required a coordinated team approach including a high-calorie and low-protein diet. Both patients had elevated leucine levels in the post-partum period - one due to mastitis and the other due to poor dietary and supplement compliance combined with uterine involution. On later review, leucine had returned to pre-pregnancy levels. Both infants were unaffected and have made normal developmental progress in the subsequent 1 to 2 years.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Successful pregnancy in maple syrup urine disease: a case report and review of the literature.Nutr J. 2018 May 12;17(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12937-018-0357-7. Nutr J. 2018. PMID: 29753318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term metabolic follow-up and clinical outcome of 35 patients with maple syrup urine disease.J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017 Nov;40(6):783-792. doi: 10.1007/s10545-017-0083-x. Epub 2017 Sep 13. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017. PMID: 28905140
-
Diagnosis and treatment of maple syrup disease: a study of 36 patients.Pediatrics. 2002 Jun;109(6):999-1008. doi: 10.1542/peds.109.6.999. Pediatrics. 2002. PMID: 12042535
-
Predictors of acute metabolic decompensation in children with maple syrup urine disease at the emergency department.Eur J Pediatr. 2020 Jul;179(7):1107-1114. doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03602-x. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Eur J Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32048023
-
[Maple syrup urine disease of neonates: report of two cases and review of literature].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010 Sep;48(9):680-4. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21092528 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Successful pregnancy in maple syrup urine disease: a case report and review of the literature.Nutr J. 2018 May 12;17(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s12937-018-0357-7. Nutr J. 2018. PMID: 29753318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pregnancy in an adolescent with maple syrup urine disease: Case report.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021 Mar 26;27:100745. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2021.100745. eCollection 2021 Jun. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2021. PMID: 33868929 Free PMC article.
-
Organic Aciduria Disorders in Pregnancy: An Overview of Metabolic Considerations.Metabolites. 2023 Apr 4;13(4):518. doi: 10.3390/metabo13040518. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 37110176 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful Pregnancy in a Woman with Maple Syrup Urine Disease: Case Report.JIMD Rep. 2015;21:103-7. doi: 10.1007/8904_2014_401. Epub 2015 Feb 27. JIMD Rep. 2015. PMID: 25720565 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of pregnancy on inborn errors of metabolism.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2018 Mar;19(1):13-33. doi: 10.1007/s11154-018-9455-2. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2018. PMID: 30198059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nobukuni Y, Mitsubuchi H, Akaboshi I, et al. Maple syrup urine disease. Complete defect of the E1 beta subunit of the branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex due to a deletion of an 11-bp repeat sequence which encodes a mitochondrial targeting leader peptide in a family with the disease. J Clin Invest. 1991;87(5):1862–1866. doi: 10.1172/JCI115209. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

