Biosynthesis of ionotropic acetylcholine receptors requires the evolutionarily conserved ER membrane complex
- PMID: 23431131
- PMCID: PMC3600456
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1216154110
Biosynthesis of ionotropic acetylcholine receptors requires the evolutionarily conserved ER membrane complex
Abstract
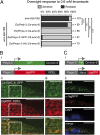
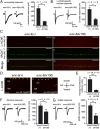
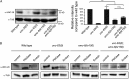
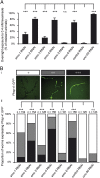
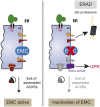
The number of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (AChRs) present in the plasma membrane of muscle and neuronal cells is limited by the assembly of individual subunits into mature pentameric receptors. This process is usually inefficient, and a large number of the synthesized subunits are degraded by endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated degradation. To identify cellular factors required for the synthesis of AChRs, we performed a genetic screen in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans for mutants with decreased sensitivity to the cholinergic agonist levamisole. We isolated a partial loss-of-function allele of ER membrane protein complex-6 (emc-6), a previously uncharacterized gene in C. elegans. emc-6 encodes an evolutionarily conserved 111-aa protein with two predicted transmembrane domains. EMC-6 is ubiquitously expressed and localizes to the ER. Partial inhibition of EMC-6 caused decreased expression of heteromeric levamisole-sensitive AChRs by destabilizing unassembled subunits in the ER. Inhibition of emc-6 also reduced the expression of homomeric nicotine-sensitive AChRs and GABAA receptors in C. elegans muscle cells. emc-6 is orthologous to the yeast and human EMC6 genes that code for a component of the recently identified ER membrane complex (EMC). Our data suggest this complex is required for protein folding and is connected to ER-associated degradation. We demonstrated that inactivation of additional EMC members in C. elegans also impaired AChR synthesis and induced the unfolded protein response. These results suggest that the EMC is a component of the ER folding machinery. AChRs might provide a valuable proxy to decipher the function of the EMC further.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A transmembrane protein required for acetylcholine receptor clustering in Caenorhabditis elegans.Nature. 2004 Sep 30;431(7008):578-82. doi: 10.1038/nature02893. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15457263 Free PMC article.
-
CRELD1 is an evolutionarily-conserved maturational enhancer of ionotropic acetylcholine receptors.Elife. 2018 Nov 7;7:e39649. doi: 10.7554/eLife.39649. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30407909 Free PMC article.
-
A single immunoglobulin-domain protein required for clustering acetylcholine receptors in C. elegans.EMBO J. 2011 Feb 16;30(4):706-18. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2010.355. Epub 2011 Jan 21. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21252855 Free PMC article.
-
ER membrane complex (EMC): Structure, functions, and roles in diseases.FASEB J. 2024 Mar 31;38(6):e23539. doi: 10.1096/fj.202302266R. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 38498340 Review.
-
Functional genomics of ionotropic acetylcholine receptors in Caenorhabditis elegans and Drosophila melanogaster.Novartis Found Symp. 2002;245:240-57; discussion 257-60, 261-4. Novartis Found Symp. 2002. PMID: 12027012 Review.
Cited by
-
The endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein complex localizes to the mitochondrial - endoplasmic reticulum interface and its subunits modulate phospholipid biosynthesis in Trypanosoma brucei.PLoS Pathog. 2022 May 2;18(5):e1009717. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009717. eCollection 2022 May. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 35500022 Free PMC article.
-
The ER Membrane Protein Complex Promotes Biogenesis of Dengue and Zika Virus Non-structural Multi-pass Transmembrane Proteins to Support Infection.Cell Rep. 2019 May 7;27(6):1666-1674.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.04.051. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31067454 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits from parasitic nematodes in Caenorhabditis elegans.Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2015 Nov;204(1):44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2015.12.006. Epub 2015 Dec 30. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26747395 Free PMC article.
-
The ER membrane protein complex is a transmembrane domain insertase.Science. 2018 Jan 26;359(6374):470-473. doi: 10.1126/science.aao3099. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Science. 2018. PMID: 29242231 Free PMC article.
-
De novo variants in EMC1 lead to neurodevelopmental delay and cerebellar degeneration and affect glial function in Drosophila.Hum Mol Genet. 2022 Sep 29;31(19):3231-3244. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddac053. Hum Mol Genet. 2022. PMID: 35234901 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Millar NS, Gotti C. Diversity of vertebrate nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2009;56(1):237–246. - PubMed
-
- Jensen TJ, et al. Multiple proteolytic systems, including the proteasome, contribute to CFTR processing. Cell. 1995;83(1):129–135. - PubMed
-
- Merlie JP, Lindstrom J. Assembly in vivo of mouse muscle acetylcholine receptor: Identification of an alpha subunit species that may be an assembly intermediate. Cell. 1983;34(3):747–757. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

