Combined targeting of MEK and PI3K/mTOR effector pathways is necessary to effectively inhibit NRAS mutant melanoma in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 23431193
- PMCID: PMC3593920
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1216013110
Combined targeting of MEK and PI3K/mTOR effector pathways is necessary to effectively inhibit NRAS mutant melanoma in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
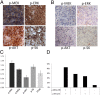
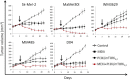
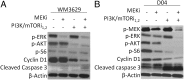
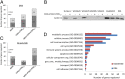
Activating mutations in the neuroblastoma rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog (NRAS) gene are common genetic events in malignant melanoma being found in 15-25% of cases. NRAS is thought to activate both mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) and PI3K signaling in melanoma cells. We studied the influence of different components on the MAP/extracellular signal-regulated (ERK) kinase (MEK) and PI3K/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-signaling cascade in NRAS mutant melanoma cells. In general, these cells were more sensitive to MEK inhibition compared with inhibition in the PI3K/mTOR cascade. Combined targeting of MEK and PI3K was superior to MEK and mTOR1,2 inhibition in all NRAS mutant melanoma cell lines tested, suggesting that PI3K signaling is more important for cell survival in NRAS mutant melanoma when MEK is inhibited. However, targeting of PI3K/mTOR1,2 in combination with MEK inhibitors is necessary to effectively abolish growth of NRAS mutant melanoma cells in vitro and regress xenografted NRAS mutant melanoma. Furthermore, we showed that MEK and PI3K/mTOR1,2 inhibition is synergistic. Expression analysis confirms that combined MEK and PI3K/mTOR1,2 inhibition predominantly influences genes in the rat sarcoma (RAS) pathway and growth factor receptor pathways, which signal through MEK/ERK and PI3K/mTOR, respectively. Our results suggest that combined targeting of the MEK/ERK and PI3K/mTOR pathways has antitumor activity and might serve as a therapeutic option in the treatment of NRAS mutant melanoma, for which there are currently no effective therapies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Schubbert S, Shannon K, Bollag G. Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(4):295–308. - PubMed
-
- Diaz-Flores E, Shannon K. Targeting oncogenic Ras. Genes Dev. 2007;21(16):1989–1992. - PubMed
-
- Kratz CP, et al. Germline mutations in components of the Ras signaling pathway in Noonan syndrome and related disorders. Cell Cycle. 2006;5(15):1607–1611. - PubMed
-
- Ball NJ, et al. Ras mutations in human melanoma: A marker of malignant progression. J Invest Dermatol. 1994;102(3):285–290. - PubMed
-
- Curtin JA, et al. Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(20):2135–2147. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

