The Potential Role of the cABR in Assessment and Management of Hearing Impairment
- PMID: 23431313
- PMCID: PMC3572655
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/604729
The Potential Role of the cABR in Assessment and Management of Hearing Impairment
Abstract
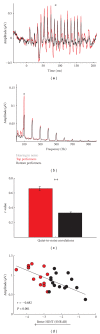
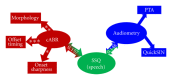
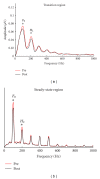
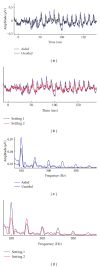
Hearing aid technology has improved dramatically in the last decade, especially in the ability to adaptively respond to dynamic aspects of background noise. Despite these advancements, however, hearing aid users continue to report difficulty hearing in background noise and having trouble adjusting to amplified sound quality. These difficulties may arise in part from current approaches to hearing aid fittings, which largely focus on increased audibility and management of environmental noise. These approaches do not take into account the fact that sound is processed all along the auditory system from the cochlea to the auditory cortex. Older adults represent the largest group of hearing aid wearers; yet older adults are known to have deficits in temporal resolution in the central auditory system. Here we review evidence that supports the use of the auditory brainstem response to complex sounds (cABR) in the assessment of hearing-in-noise difficulties and auditory training efficacy in older adults.
Figures


References
-
- Gordon-Salant S, Fitzgibbons PJ, Friedman SA. Recognition of time-compressed and natural speech with selective temporal enhancements by young and elderly listeners. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research. 2007;50(5):1181–1193. - PubMed
-
- CasparyJ DM, Milbrand JC, Helfert RH. Central auditory aging: GABA changes in the inferior colliculus. Experimental Gerontology. 1995;30(3-4):349–360. - PubMed
-
- Tremblay KL, Piskosz M, Souza P. Effects of age and age-related hearing loss on the neural representation of speech cues. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2003;114(7):1332–1343. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

