Overexpression of initiator methionine tRNA leads to global reprogramming of tRNA expression and increased proliferation in human epithelial cells
- PMID: 23431330
- PMCID: PMC3677255
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.037507.112
Overexpression of initiator methionine tRNA leads to global reprogramming of tRNA expression and increased proliferation in human epithelial cells
Abstract
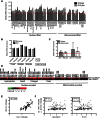
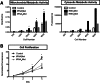
Transfer RNAs (tRNAs) are typically considered housekeeping products with little regulatory function. However, several studies over the past 10 years have linked tRNA misregulation to cancer. We have previously reported that tRNA levels are significantly elevated in breast cancer and multiple myeloma cells. To further investigate the cellular and physiological effects of tRNA overexpression, we overexpressed tRNAi(Met) in two human breast epithelial cell lines. We then determined tRNA abundance changes and performed phenotypic characterization. Overexpression of tRNAi(Met) significantly altered the global tRNA expression profile and resulted in increased cell metabolic activity and cell proliferation. Our results extend the relevance of tRNA overexpression in human cells and underscore the complexity of cellular regulation of tRNA expression.
Figures
References
-
- Agris PF, Vendeix FA, Graham WD 2007. tRNA’s wobble decoding of the genome: 40 years of modification. J Mol Biol 366: 1–13 - PubMed
-
- Alexandrov A, Chernyakov I, Gu W, Hiley SL, Hughes TR, Grayhack EJ, Phizicky EM 2006. Rapid tRNA decay can result from lack of nonessential modifications. Mol Cell 21: 87–96 - PubMed
-
- Bjornsti MA, Houghton PJ 2004. Lost in translation: Dysregulation of cap-dependent translation and cancer. Cancer Cell 5: 519–523 - PubMed
-
- Borel F, Hartlein M, Leberman R 1993. In vivo overexpression and purification of Escherichia coli tRNAser. FEBS Lett 324: 162–166 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
