Nanowire-based electrode for acute in vivo neural recordings in the brain
- PMID: 23431387
- PMCID: PMC3576334
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056673
Nanowire-based electrode for acute in vivo neural recordings in the brain
Abstract
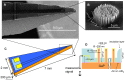
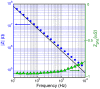
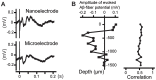
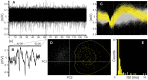
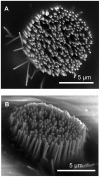
We present an electrode, based on structurally controlled nanowires, as a first step towards developing a useful nanostructured device for neurophysiological measurements in vivo. The sensing part of the electrode is made of a metal film deposited on top of an array of epitaxially grown gallium phosphide nanowires. We achieved the first functional testing of the nanowire-based electrode by performing acute in vivo recordings in the rat cerebral cortex and withstanding multiple brain implantations. Due to the controllable geometry of the nanowires, this type of electrode can be used as a model system for further analysis of the functional properties of nanostructured neuronal interfaces in vivo.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Cogan SF (2008) Neural stimulation and recording electrodes. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 10: 275–309. - PubMed
-
- Fromherz P (2003) Neuroelectronic Interfacing: Semiconductor Chips with Ion Channels, Nerve Cells, and Brain. In: Waser R, editor. Nanoelectronics and Information Technology. Berlin: Wiley-VCH. 781–810.
-
- Rutten WLC (2002) Selective electrical interfaces with the nervous system. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 4: 407–452. - PubMed
-
- Benabid AL (2007) What the future holds for deep brain stimulation. Expert Rev Med Devices 4: 895–903. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

