Gd-based macromolecules and nanoparticles as magnetic resonance contrast agents for molecular imaging
- PMID: 23432004
- PMCID: PMC3761358
- DOI: 10.2174/1568026611313040002
Gd-based macromolecules and nanoparticles as magnetic resonance contrast agents for molecular imaging
Abstract
As we move towards an era of personalized medicine, molecular imaging contrast agents are likely to see an increasing presence in routine clinical practice. Magnetic resonance (MR) imaging has garnered particular interest as a platform for molecular imaging applications due its ability to monitor anatomical changes concomitant with physiologic and molecular changes. One promising new direction in the development of MR contrast agents involves the labeling and/or loading of nanoparticles with gadolinium (Gd). These nanoplatforms are capable of carrying large payloads of Gd, thus providing the requisite sensitivity to detect molecular signatures within disease pathologies. In this review, we discuss some of the progress that has recently been made in the development of Gd-based macromolecules and nanoparticles and outline some of the physical and chemical properties that will be important to incorporate into the next generation of contrast agents, including high Gd chelate stability, high "relaxivity per particle" and "relaxivity density", and biodegradability.
Figures
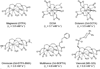

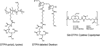

References
-
- Parmelee DJ, Walovitch RC, Ouellet HS, Lauffer RB. Preclinical Evaluation of the Pharmacokinetics, Biodistribution, and Elimination of MS-325, a Blood Pool Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Invest. Radiol. 1997;32:741–747. - PubMed
-
- Weissleder R, Kelly K, Sun EY, Shtatland T, Josephson L. Cell-specific targeting of nanoparticles by multivalent attachment of small molecules. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005;23(11):1418–1423. - PubMed
-
- Caravan P. Strategies for increasing the sensitivity of gadolinium based MRI contrast agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2006;35(6):512–523. - PubMed
-
- Botta M, Tei L. Relaxivity Enhancement in Macromolecular and Nanosized GdIII-Based MRI Contrast Agents. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012;12:1945–1960.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

