Severe and uncontrolled adult asthma is associated with vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency
- PMID: 23432854
- PMCID: PMC3648461
- DOI: 10.1186/1465-9921-14-25
Severe and uncontrolled adult asthma is associated with vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency
Abstract
Background: Vitamin D has effects on the innate and adaptive immune system. In asthmatic children low vitamin D levels are associated with poor asthma control, reduced lung function, increased medication intake, and exacerbations. Little is known about vitamin D in adult asthma patients or its association with asthma severity and control.
Methods: Clinical parameters of asthma control and 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) serum concentrations were evaluated in 280 adult asthma patients (mean ± SD: 45.0 ± 13.8 yrs., 40% male, FEV1 74.9 ± 23.4%, 55% severe, 51% uncontrolled).
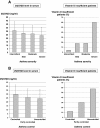
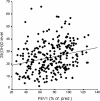
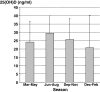
Results: 25(OH)D concentrations in adult asthmatics were low (25.6 ±11.8 ng/ml) and vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency (vitamin D <30 ng/ml) was common (67%). 25(OH)D levels were related to asthma severity (intermittent: 31.1 ± 13.0 ng/ml, mild: 27.3 ± 11.9 ng/ml, moderate: 26.5 ± 12.0 ng/ml, severe: 24.0 ± 11.8 ng/ml, p = 0.046) and control (controlled: 29.5 ± 12.5 ng/ml, partly controlled 25.9 ± 10.8 ng/ml, uncontrolled: 24.2 ± 11.8 ng/ml, p = 0.030). The frequency of vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency was significantly higher in patients with severe or uncontrolled asthma and was associated with a lower FEV1 (vitamin D <30 vs. ≥30 ng/ml 2.3 ± 0.9 L vs. 2.7 ± 1.0 L, p = 0.006), higher levels of exhaled NO (45 ± 46 ppb vs. 31 ± 37 ppb, p = 0.023), a higher BMI (28.3 ± 6.2 vs. 25.1 ± 3.9, p < 0.001), and sputum eosinophilia (5.1 ± 11.8% vs. 0.5 ± 1.0%, p = 0.005). The use of oral corticosteroids or sputum eosinophilia was associated with a 20% or 40% higher risk of vitamin D insufficiency or deficiency.
Conclusions: 25(OH)D levels below 30 ng/ml are common in adult asthma and most pronounced in patients with severe and/or uncontrolled asthma, supporting the hypothesis that improving suboptimal vitamin D status might be effective in prevention and treatment of asthma.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prevalence, determinants and clinical correlates of vitamin D deficiency in adults with inhaled corticosteroid-treated asthma in London, UK.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Jan;175:88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.11.004. Epub 2016 Nov 5. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 27825992
-
Association Between Severe Vitamin D Deficiency, Lung Function and Asthma Control.Arch Bronconeumol. 2017 Apr;53(4):186-191. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2016.09.010. Epub 2017 Mar 18. Arch Bronconeumol. 2017. PMID: 28320552 English, Spanish.
-
25-hydroxy vitamin D levels are associated with childhood asthma in a population-based study in Peru.Clin Exp Allergy. 2015 Jan;45(1):273-82. doi: 10.1111/cea.12311. Clin Exp Allergy. 2015. PMID: 24666565 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association between vitamin D status and asthma control: A meta-analysis of randomized trials.Respir Med. 2019 Apr;150:85-94. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 Feb 21. Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 30961957 Review.
-
[Review of the concept of vitamin D "sufficiency and insufficiency"].Nefrologia. 2003;23 Suppl 2:73-7. Nefrologia. 2003. PMID: 12778859 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Relation between vitamin D deficiency and Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonization in patients with bronchiectasis.BMC Pulm Med. 2025 Feb 14;25(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03548-6. BMC Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 39953443 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D and Immunity in Infants and Children.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 27;12(5):1233. doi: 10.3390/nu12051233. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32349265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asthma control status in pregnancy, body mass index, and maternal vitamin D levels.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Nov;140(5):1453-1456.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2017.03.053. Epub 2017 Jun 9. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28606587 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
1,25D3 prevents CD8(+)Tc2 skewing and asthma development through VDR binding changes to the Cyp11a1 promoter.Nat Commun. 2016 Jan 11;7:10213. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10213. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 26750596 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Serum 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D Levels and the Prevalence of Adult-Onset Asthma.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018 May 29;15(6):1103. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15061103. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29843458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma. GINA Report, Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention - revised 2010. 2010. Available at: [ http://www.ginasthma.org]
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

