Posterior spinal artery syndrome showing marked swelling of the spinal cord: a clinico-pathological study
- PMID: 23433332
- PMCID: PMC3555103
- DOI: 10.1179/2045772312Y.0000000017
Posterior spinal artery syndrome showing marked swelling of the spinal cord: a clinico-pathological study
Abstract
Objective: To describe a rare autopsy case of posterior spinal artery syndrome with marked swelling of the spinal cord, an unusually subacute onset and short clinical course.
Methods: Case report.
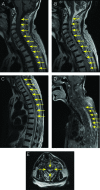
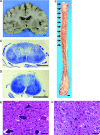
Findings: An 84-year-old Japanese woman presented with bilateral muscle weakness of the lower legs and sensory disturbance 1 week after head contusion. Neurological findings worsened gradually. She developed phrenic nerve paralysis and died of respiratory failure 6 weeks after the onset of neurological symptoms. On pathological examination, the spinal cord was markedly swollen in the cervical and upper thoracic segments. Microscopically, there was loss of myelin sheath in the bilateral posterior columns and neuronal loss of the posterior horns in all of the spinal segments. However, findings were unremarkable in the bilateral anterior columns and bilateral anterior horns in most of the spinal segments. Posterior spinal arteries had no stenosis, occlusion, or thrombosis. We considered that pathogenesis was infarction associated with head injury.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first report of a case of posterior spinal artery syndrome with a markedly swollen spinal cord and poor prognosis.
Figures
References
-
- Hegedüs K, Fekete I. Case report of infarction in the region of the posterior spinal arteries. Eur Arch Psych Neurol Sci. 1984;234(4):281–4 - PubMed
-
- Williamson RT. Spinal softening limited to the parts supplied by the posterior arterial system of the cord. Lancet. 1895;2(3757):520–1
-
- Chung MF. Thrombosis of the spinal vessels in sudden syphilitic paraplegia. Arch Neurol Psychiatry. 1926;16(6):761–71
-
- Henneberg R. Reine vaskulare, spinale Lues. Berl Klin Wochenschr. 1920;57(43):1026–32
-
- Hinrichs U. Myelodegeneratio non specifica bei Luikern. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1928;106(1–6):1–12
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
