Regulation of nuclear factor-κB in autoimmunity
- PMID: 23434408
- PMCID: PMC3664242
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2013.01.004
Regulation of nuclear factor-κB in autoimmunity
Abstract
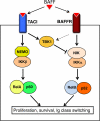
Nuclear factor (NF)-κB transcription factors are pivotal regulators of innate and adaptive immune responses, and perturbations of NF-κB signaling contribute to the pathogenesis of immunological disorders. NF-κB is a well-known proinflammatory mediator, and its deregulated activation is associated with the chronic inflammation of autoimmune diseases. Paradoxically, NF-κB plays a crucial role in the establishment of immune tolerance, including both central tolerance and the peripheral function of regulatory T (Treg) cells. Thus, defective or deregulated activation of NF-κB may contribute to autoimmunity and inflammation, highlighting the importance of tightly controlled NF-κB signaling. This review focuses on recent progress regarding NF-κB regulation and its association with autoimmunity.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Theofilopoulos AN. The basis of autoimmunity: Part I. Mechanisms of aberrant self-recognition. Immunol. Today. 1995;16:90–98. - PubMed
-
- Pai S, Thomas R. Immune deficiency or hyperactivity-Nf-kappab illuminates autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2008;31:245–251. - PubMed
-
- Schmitz ML, Krappmann D. Controlling NF-kappaB activation in T cells by costimulatory receptors. Cell. Death Differ. 2006;13:834–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

