The RNA-binding region of human TRBP interacts with microRNA precursors through two independent domains
- PMID: 23435228
- PMCID: PMC3627579
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt086
The RNA-binding region of human TRBP interacts with microRNA precursors through two independent domains
Abstract
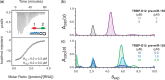
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression through RNA interference. Human miRNAs are generated through a series of enzymatic processing steps. The precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) is recognized and cleaved by a complex containing Dicer and several non-catalytic accessory proteins. HIV TAR element binding protein (TRBP) is a constituent of the Dicer complex, which augments complex stability and potentially functions in substrate recognition and product transfer to the RNA-induced silencing complex. Here we have analysed the interaction between the RNA-binding region of TRBP and an oncogenic human miRNA, miR-155, at different stages in the biogenesis pathway. We show that the region of TRBP that binds immature miRNAs comprises two independent double-stranded RNA-binding domains connected by a 60-residue flexible linker. No evidence of contact between the two double-stranded RNA-binding domains was observed either in the apo- or RNA-bound state. We establish that the RNA-binding region of TRBP interacts with both pre-miR-155 and the miR-155/miR-155* duplex through the same binding surfaces and with similar affinities, and that two protein molecules can simultaneously interact with each immature miRNA. These data suggest that TRBP could play a role before and after processing of pre-miRNAs by Dicer.
Figures
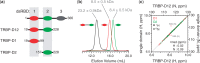
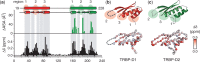
 + (ΔδN/6.5)2]½, where ΔδX is the difference in chemical shift between apo- and RNA-bound spectra (39). Prolines and unassigned residues have been given values of −0.05 and −0.1 ppm, respectively. For comparison, the change in accessible surface area (ΔASA) when TRBP-D2 forms a complex with dsRNA is shown (green). ΔASA were calculated using the POPS* server (46) from 3ADL (18). The boundaries of secondary structure elements were taken from the 3D structures of TRBP-D1 [3LLH; (31)] and TRBP-D2 [3ADL; (18)]; (b,c) TOP: cartoon representation of the 3D structures of TRBP-D1 and TRBP-D2 showing the three regions in canonical dsRBDs that are implicated in dsRNA binding; (b,c) BOTTOM: Δδ values plotted on the respective 3D structures. Each amide nitrogen is represented by a sphere and coloured according to the Δδ scale provided. The β2/3 loop was not resolved in the 3D structure of TRBP-D1 and is shown by a broken line.
+ (ΔδN/6.5)2]½, where ΔδX is the difference in chemical shift between apo- and RNA-bound spectra (39). Prolines and unassigned residues have been given values of −0.05 and −0.1 ppm, respectively. For comparison, the change in accessible surface area (ΔASA) when TRBP-D2 forms a complex with dsRNA is shown (green). ΔASA were calculated using the POPS* server (46) from 3ADL (18). The boundaries of secondary structure elements were taken from the 3D structures of TRBP-D1 [3LLH; (31)] and TRBP-D2 [3ADL; (18)]; (b,c) TOP: cartoon representation of the 3D structures of TRBP-D1 and TRBP-D2 showing the three regions in canonical dsRBDs that are implicated in dsRNA binding; (b,c) BOTTOM: Δδ values plotted on the respective 3D structures. Each amide nitrogen is represented by a sphere and coloured according to the Δδ scale provided. The β2/3 loop was not resolved in the 3D structure of TRBP-D1 and is shown by a broken line.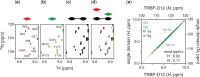

References
-
- Zamore PD, Haley B. Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science. 2005;309:1519–1524. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q, Paroo Z. Biochemical principles of small RNA pathways. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2010;79:295–319. - PubMed
-
- Gatignol A, Buckler-White A, Berkhout B, Jeang KT. Characterization of a human TAR RNA-binding protein that activates the HIV-1 LTR. Science. 1991;251:1597–1600. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

