Induction of heme oxygenase-1 protects mouse liver from apoptotic ischemia/reperfusion injury
- PMID: 23435964
- PMCID: PMC5560494
- DOI: 10.1007/s10495-013-0814-x
Induction of heme oxygenase-1 protects mouse liver from apoptotic ischemia/reperfusion injury
Abstract
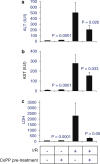
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury is the main cause of primary graft dysfunction of liver allografts. Cobalt-protoporphyrin (CoPP)-dependent induction of heme oxygenase (HO)-1 has been shown to protect the liver from I/R injury. This study analyzes the apoptotic mechanisms of HO-1-mediated cytoprotection in mouse liver exposed to I/R injury. HO-1 induction was achieved by the administration of CoPP (1.5 mg/kg body weight i.p.). Mice were studied in in vivo model of hepatic segmental (70 %) ischemia for 60 min and reperfusion injury. Mice were randomly allocated to four main experimental groups (n = 10 each): (1) A control group undergoing sham operation. (2) Similar to group 1 but with the administration of CoPP 72 h before the operation. (3) Mice undergoing in vivo hepatic I/R. (4) Similar to group 3 but with the administration of CoPP 72 h before ischemia induction. When compared with the I/R mice group, in the I/R+CoPP mice group, the increased hepatic expression of HO-1 was associated with a significant reduction in liver enzyme levels, fewer apoptotic hepatocytes cells were identified by morphological criteria and by immunohistochemistry for caspase-3, there was a decreased mean number of proliferating cells (positively stained for Ki67), and a reduced hepatic expression of: C/EBP homologous protein (an index of endoplasmic reticulum stress), the NF-κB's regulated genes (CIAP2, MCP-1 and IL-6), and increased hepatic expression of IκBa (the inhibitory protein of NF-κB). HO-1 over-expression plays a pivotal role in reducing the hepatic apoptotic IR injury. HO-1 may serve as a potential target for therapeutic intervention in hepatic I/R injury during liver transplantation.
Figures





References
-
- Clavien PA, Harvey PR, Strasberg SM. Preservation and reperfusion injuries in liver allografts. An overview and synthesis of current studies. Transplantation. 1992;53:957–978. - PubMed
-
- Jaeschke H. Preservation injury: mechanisms, prevention and consequences. J Hepatol. 1996;25:774–780. - PubMed
-
- Kojima Y, Suzuki S, Tsuchiya Y, Konno H, Baba S, Nakamura S. Regulation of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine responses by kupffer cells in endotoxin-enhanced reperfusion injury after total hepatic ischemia. Transpl Int. 2003;16:231–240. - PubMed
-
- Nathan C. Points of control in inflammation. Nature. 2002;420:846–852. - PubMed
-
- Geuken E, Buis CI, Visser DS, et al. Expression of heme oxygenase-1 in human livers before transplantation correlates with graft injury and function after transplantation. Am J Transpl. 2005;5:1875. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

