Emerging and mechanism-based therapies for recurrent or metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma
- PMID: 23436166
- PMCID: PMC3651762
- DOI: 10.1007/s11864-013-0225-9
Emerging and mechanism-based therapies for recurrent or metastatic Merkel cell carcinoma
Abstract
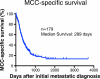
Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is a rare but aggressive neuroendocrine skin cancer with a disease-specific mortality of approximately 40 %. The association of MCC with a recently discovered polyomavirus, combined with the increased incidence and mortality of MCC among immunocompromised patients, highlight the importance of the immune system in controlling this cancer. Initial management of MCC is summarized within the NCCN guidelines and in recently published reviews. The high rate of recurrent and metastatic disease progression in MCC, however, presents a major challenge in a cancer that lacks mechanism-based, disease-specific therapies. Traditional treatment approaches have focused on cytotoxic chemotherapy that, despite frequent initial efficacy, rarely provides durable responses and has high morbidity among the elderly. In addition, the immunosuppressive nature of chemotherapy is of concern when treating a virus-associated cancer for which survival is unusually tightly linked to immune function. With a median survival of 9.6 months after development of an initial metastasis (n = 179, described herein), and no FDA-approved agents for this cancer, there is an urgent need for more effective treatments. We review diverse management options for patients with advanced MCC, with a focus on emerging and mechanism-based therapies, some of which specifically target persistently expressed viral antigens. These treatments include single-dose radiation and novel immunotherapies, some of which are in clinical trials. Due to their encouraging efficacy, low toxicity, and lack of immune suppression, these therapies may offer viable alternatives to traditional cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Figures
References
-
- Albores-Saavedra J, Batich K, Chable-Montero F, et al. Merkel cell carcinoma demographics, morphology, and survival based on 3870 cases: a population based study. J Cutan Pathol. 2010;37(1):20–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

