Nuclear receptor NR4A2 orchestrates Th17 cell-mediated autoimmune inflammation via IL-21 signalling
- PMID: 23437182
- PMCID: PMC3578929
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056595
Nuclear receptor NR4A2 orchestrates Th17 cell-mediated autoimmune inflammation via IL-21 signalling
Abstract
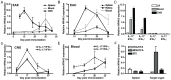
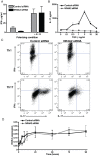
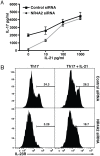
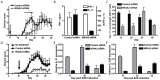
IL-17-producing CD4(+) T helper 17 (Th17) cells are pathogenic in a range of human autoimmune diseases and corresponding animal models. We now demonstrate that such T cells infiltrating the target organ during the induction of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) and experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis (EAU) specifically express NR4A2. Further, we reveal a critical involvement of NR4A2 in Th17 cell functions and Th17 cell-driven autoimmune diseases. When NR4A2 expression was blocked with siRNA, full Th17 differentiation was prevented in vitro: although cells expressed the master Th17 regulator, RORγt, they expressed reduced levels of IL-23R and were unable to produce IL-17 and IL-21. Notably, Th17 differentiation in the absence of NR4A2 was restored by exogenous IL-21, indicating that NR4A2 controls full maturation of Th17 cells via autocrine IL-21 signalling. Preventing NR4A2 expression in vivo by systemic treatment with NR4A2-specific siRNA also reduced Th17 effector responses and furthermore protected mice from EAE induction. In addition, the lack of disease was associated with a reduction in autocrine IL-21 production and IL-23R expression. Similar modulation of NR4A2 expression was also effective as an intervention, reversing established autoimmune responses and ameliorating clinical disease symptoms. Thus, NR4A2 appears to control Th17 differentiation and so plays an essential role in the development of Th17-mediated autoimmune disease. As NR4A2 is also upregulated during human autoimmune disease, targeting NR4A2 may provide a new therapeutic approach in treating autoimmune disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Sospedra M, Martin R (2005) Immunology of multiple sclerosis. Annu Rev Immunol 23: 683–747. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

