Arthropod-borne flaviviruses and RNA interference: seeking new approaches for antiviral therapy
- PMID: 23439025
- PMCID: PMC7149629
- DOI: 10.1016/B978-0-12-408116-1.00004-5
Arthropod-borne flaviviruses and RNA interference: seeking new approaches for antiviral therapy
Abstract
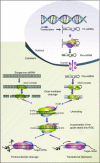
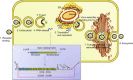
Flaviviruses are the most prevalent arthropod-borne viruses worldwide, and nearly half of the 70 Flavivirus members identified are human pathogens. Despite the huge clinical impact of flaviviruses, there is no specific human antiviral therapy available to treat infection with any of the flaviviruses. Therefore, there is a continued search for novel therapies, and this review describes the current knowledge on the usage of RNA interference (RNAi) in combating flavivirus infections. RNAi is a process of sequence-specific gene silencing triggered by double-stranded RNA. Antiviral RNAi strategies against arthropod-borne flaviviruses have been reported and although several hurdles must be overcome to employ this technology in clinical applications, they potentially represent a new therapeutic tool.
2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved
Figures
References
-
- Adelman Z.N., Blair C.D., Carlson J.O., Beaty B.J., Olson K.E. Sindbis virus-induced silencing of dengue viruses in mosquitoes. Insect Molecular Biology. 2001;10(3):265–273. - PubMed
-
- Amarzguioui M., Rossi J.J., Kim D. Approaches for chemically synthesized siRNA and vector-mediated RNAi. FEBS Letters. 2005;579(26):5974–5981. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

