High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and tumor necrotizing factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) after on- and off- pump coronary artery bypass grafting
- PMID: 23439767
- PMCID: PMC3484567
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and tumor necrotizing factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) after on- and off- pump coronary artery bypass grafting
Abstract
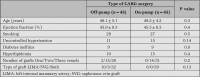
Introduction: Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is one of the most frequently performed operations around the world. The aim of this study is to evaluate high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) differences between on-pump and off-pump coronary surgery.
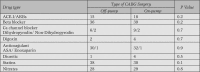
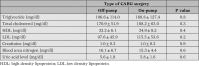
Methods: In this prospective study, 90 patients with coronary artery disease referred for CABG were enrolled from July 2006-November 2007. Levels of hs-CRP and TNF-alpha were measured by ELISA using commercial kits
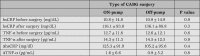
Results: hs-CRP levels significantly (p<0.001) increase after CABG. But no difference between off-pump and on-pump groups was noted for hs-CRP and TNF-alpha levels (p=0.4, p=0.8).
Conclusions: There was no difference in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) and TNF-alpha between on-pump and off-pump CABG surgery.
Keywords: C-reactive protein (CRP); cardiopulmonary bypass; coronary artery bypass grafting; off-pump; on-pump; tumor necrotizing factor-alpha (TNF-alpha).
Figures
References
-
- Howson CP, Fineberg HV, Bloom BR. The pursuit of global health: the relevance of engagement for developed countries. Lancet. 1998;35:586–590. - PubMed
-
- Yacoub M. Off-pump coronary bypass surgery: in search of an identity. Circulation. 2001;104:1743–1745. - PubMed
-
- Franke A, Lante W, Fackeldey V. et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines after different kinds of cardio-thoracic surgical procedures: is what we see what we know? Eur J Cardiothorac. 2005;28:569–575. - PubMed
-
- Levy JH, Tanaka KA. Inflammatory response to cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75:715–720. - PubMed
-
- Cleveland JC jr, Shroyer AL, Chen AY. et al. Off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting decreases risk-adjusted mortality and morbidity. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72:1282–1288. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous