Hypothalamic ventromedial COUP-TFII protects against hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure
- PMID: 23440210
- PMCID: PMC3600439
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1219262110
Hypothalamic ventromedial COUP-TFII protects against hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure
Abstract
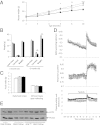
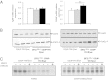
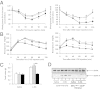
The nuclear receptor Chicken Ovalbumin Upstream Promoter-Transcription Factor II (COUP-TFII) is an important coordinator of glucose homeostasis through its function in different organs such as the endocrine pancreas, adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and liver. Recently we have demonstrated that COUP-TFII expression in the hypothalamus is restricted to a subpopulation of neurons expressing the steroidogenic factor 1 transcription factor, known to play a crucial role in glucose homeostasis. To understand the functional significance of COUP-TFII expression in the steroidogenic factor 1 neurons, we generated hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus-specific COUP-TFII KO mice using the cyclization recombination/locus of X-overP1 technology. The heterozygous mutant mice display insulin hypersensitivity and a leaner phenotype associated with increased energy expenditure and similar food intake. These mutant mice also present a defective counterregulation to hypoglycemia with altered glucagon secretion. Moreover, the mutant mice are more likely to develop hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in response to recurrent hypoglycemic or glucopenic events. Therefore, COUP-TFII expression levels in the ventromedial nucleus are keys in the ability to resist the onset of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dhillon H, et al. Leptin directly activates SF1 neurons in the VMH, and this action by leptin is required for normal body-weight homeostasis. Neuron. 2006;49(2):191–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

