Emotional and non-emotional pathways to impulsive behavior and addiction
- PMID: 23441001
- PMCID: PMC3578351
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00043
Emotional and non-emotional pathways to impulsive behavior and addiction
Erratum in
- Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:411
Abstract
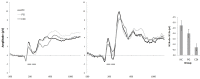
Impulsivity is tightly linked to addiction. However, there are several pathways by means of which impulsive individuals are more prone to become addicts, or to suffer an addiction more intensely and for a longer period. One of those pathways involves an inadequate appraisal or regulation of positive and negative emotions, leading to lack of control over hazardous behaviors, and inappropriate decisions. In the present work, we assessed cocaine-dependent individuals (CDI; n = 20), pathological gamblers (PG; n = 21), and healthy controls (HC; n = 23) in trait impulsivity measures (UPPS-P model's dimensions), and decision-making tasks (Go/No-go; delay-discounting task). During the Go/No-go task, electroencephalographic (EEG) activity was recorded, and Go/No-go stimuli-evoked potentials (ERP) were extracted. Theory-driven ERP analyses focused on the No-go > Go difference in the N2 ERP. Our results show that negative urgency is one of the several psychological features that distinguish addicts from HC. Nevertheless, among the dimensions of trait impulsivity, negative urgency is unique at independently covarying with gambling over-pathologization in the PG sample. Cocaine-dependent individuals performed more poorly than gamblers in the Go/No-go task, and showed abnormal Go/No-go stimuli-evoked potentials. The difference between the No-go stimulus-evoked N2, and the Go one was attenuated by severity and intensity of chronic cocaine use. Emotional dimensions of impulsivity, however, did not influence Go/No-go performance.
Keywords: Go/No-go; N2 ERP; UPPS-P; addiction; decision-making; delay discounting; emotion; impulsivity.
Figures
References
-
- Albein-Urios N., Martinez-González J. M., Lozano O., Clark L., Verdejo-García A. (2012a). Comparison of impulsivity and working memory in cocaine addiction and pathological gambling: implications for cocaine-induced neurotoxicity. Drug Alcohol Depend. 126, 1–6 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.03.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Albein-Urios N., Verdejo-Román J., Asensio S., Soriano-Mas C., Martínez-González J. M., Verdejo-García A. (2012b). Re-appraisal of negative emotions in cocaine dependence: dysfunctional corticolimbic activation and connectivity. Addict. Biol. 10, 1369–1600 10.1111/j.1369-1600.2012.00497.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barratt E. S. (1993). Impulsivity: integrating cognitive, behavioral, biological and environmental data, in The Impulsive Client: Theory, Research, and Treatment, eds McCowan W., Johnson J., Shure M. (Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; ), 39–56
-
- Belouchrani A., Abed Meraim K., Cardoso J.-F., Moulines E. (1993). Second-order blind separation of temporally correlated sources, in Proceeding of the International Conference on Digital Signal Processing, (Cyprus: ), 346–351
-
- Belouchrani A., Abed Meraim K., Cardoso J.-F., Moulines E. (1997). A blind source separation technique based on second order statistics. IEES Trans. Signal Process. 45, 434–444
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

