Inhibition of the growth of patient-derived pancreatic cancer xenografts with the MEK inhibitor trametinib is augmented by combined treatment with the epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib
- PMID: 23441129
- PMCID: PMC3579317
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.121712
Inhibition of the growth of patient-derived pancreatic cancer xenografts with the MEK inhibitor trametinib is augmented by combined treatment with the epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib
Abstract
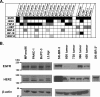
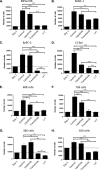
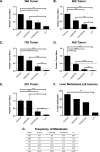
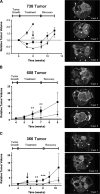
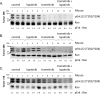
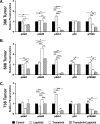
Mutations of the oncogene KRAS are important drivers of pancreatic cancer progression. Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and human EGFR2 (HER2) is observed frequent in pancreatic adenocarcinomas. Because of co-activation of these two signaling pathways, we assessed the efficacy of inhibition of EGFR/HER2 receptors and the downstream KRAS effector, mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular-signal regulated kinase (ERK) kinase 1 and 2 (MEK1/2), on pancreatic cancer proliferation in vitro and in a murine orthotopic xenograft model. Treatment of established and patient-derived pancreatic cancer cell lines with the MEK1/2 inhibitor trametinib (GSK1120212) inhibited proliferation, and addition of the EGFR/HER2 inhibitor lapatinib enhanced the inhibition elicited by trametinib in three of eight cell lines. Importantly, in the orthotopic xenograft model, treatment with lapatinib and trametinib resulted in significantly enhanced inhibition of tumor growth relative to trametinib treatment alone in four of five patient-derived tumors tested and was, in all cases, significantly more effective in reducing the size of established tumors than treatment with lapatinib or trametinib alone. Acute treatment of established tumors with trametinib resulted in an increase in AKT2 phosphorylation that was blunted in mice treated with both trametinib and lapatinib. These data indicate that inhibition of the EGFR family receptor signaling may contribute to the effectiveness of MEK1/2 inhibition of tumor growth possibly through the inhibition of feedback activation of receptor tyrosine kinases in response to inhibition of the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway. These studies provide a rationale for assessing the co-inhibition of these pathways in the treatment of pancreatic cancer patients.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Co-treatment with panitumumab and trastuzumab augments response to the MEK inhibitor trametinib in a patient-derived xenograft model of pancreatic cancer.Neoplasia. 2014 Jul;16(7):562-71. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2014.06.004. Neoplasia. 2014. PMID: 25117978 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitization of epidermal growth factor receptor/HER2-positive pancreatic cancer is mediated by inhibition of Akt independent of ras mutational status.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Feb 1;16(3):912-23. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1324. Epub 2010 Jan 26. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20103665 Free PMC article.
-
A novel regimen for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma targeting MEK, BCL-xL, and EGFR.Neoplasia. 2025 Jan;59:101070. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2024.101070. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Neoplasia. 2025. PMID: 39541736 Free PMC article.
-
Trametinib in the treatment of multiple malignancies harboring MEK1 mutations.Cancer Treat Rev. 2019 Dec;81:101907. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2019.101907. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019. PMID: 31715422 Review.
-
Targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and its downstream signaling pathways by natural products: A mechanistic insight.Phytother Res. 2024 May;38(5):2406-2447. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8166. Epub 2024 Mar 3. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 38433568 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthetic lethal short hairpin RNA screening reveals that ring finger protein 183 confers resistance to trametinib in colorectal cancer cells.Chin J Cancer. 2017 Jul 31;36(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s40880-017-0228-1. Chin J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28756770 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Resistance Pathways Specific to Malignancy Using Organoid Models of Pancreatic Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Nov 15;25(22):6742-6755. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-1398. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31492749 Free PMC article.
-
Drp1 Promotes KRas-Driven Metabolic Changes to Drive Pancreatic Tumor Growth.Cell Rep. 2019 Aug 13;28(7):1845-1859.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.031. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 31412251 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated fraction radiotherapy with capecitabine as neoadjuvant therapy for borderline resectable pancreatic cancer.Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2014 Jan;7(1):15-22. Gastrointest Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24558510 Free PMC article.
-
SOX2 functions as a molecular rheostat to control the growth, tumorigenicity and drug responses of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 7;7(23):34890-906. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8994. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27145457 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
