Carnosine: can understanding its actions on energy metabolism and protein homeostasis inform its therapeutic potential?
- PMID: 23442334
- PMCID: PMC3602167
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-38
Carnosine: can understanding its actions on energy metabolism and protein homeostasis inform its therapeutic potential?
Abstract
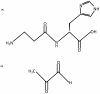
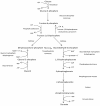
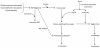
The dipeptide carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine) has contrasting but beneficial effects on cellular activity. It delays cellular senescence and rejuvenates cultured senescent mammalian cells. However, it also inhibits the growth of cultured tumour cells. Based on studies in several organisms, we speculate that carnosine exerts these apparently opposing actions by affecting energy metabolism and/or protein homeostasis (proteostasis). Specific effects on energy metabolism include the dipeptide's influence on cellular ATP concentrations. Carnosine's ability to reduce the formation of altered proteins (typically adducts of methylglyoxal) and enhance proteolysis of aberrant polypeptides is indicative of its influence on proteostasis. Furthermore these dual actions might provide a rationale for the use of carnosine in the treatment or prevention of diverse age-related conditions where energy metabolism or proteostasis are compromised. These include cancer, Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease and the complications of type-2 diabetes (nephropathy, cataracts, stroke and pain), which might all benefit from knowledge of carnosine's mode of action on human cells.
Figures
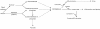
Similar articles
-
On the enigma of carnosine's anti-ageing actions.Exp Gerontol. 2009 Apr;44(4):237-42. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2008.11.001. Epub 2008 Nov 11. Exp Gerontol. 2009. PMID: 19041712
-
Carnosine, the anti-ageing, anti-oxidant dipeptide, may react with protein carbonyl groups.Mech Ageing Dev. 2001 Sep 15;122(13):1431-45. doi: 10.1016/s0047-6374(01)00272-x. Mech Ageing Dev. 2001. PMID: 11470131
-
Carnosine's inhibitory effect on glioblastoma cell growth is independent of its cleavage.Amino Acids. 2019 May;51(5):761-772. doi: 10.1007/s00726-019-02713-6. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Amino Acids. 2019. PMID: 30863889
-
Reaction of carnosine with aged proteins: another protective process?Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Apr;959:285-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb02100.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 11976203 Review.
-
Carnosine and its possible roles in nutrition and health.Adv Food Nutr Res. 2009;57:87-154. doi: 10.1016/S1043-4526(09)57003-9. Adv Food Nutr Res. 2009. PMID: 19595386 Review.
Cited by
-
Use of carnosine in the prevention of cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese individuals: study protocol for a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2021 May 13;11(5):e043680. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-043680. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33986049 Free PMC article.
-
On the use of carnosine and antioxidants: A letter from Russia.J Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 2016 Apr 21;5(3):317-9. doi: 10.5455/jice.20160409010229. eCollection 2016 Jun-Aug. J Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27366359 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
International society of sports nutrition position stand: Beta-Alanine.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015 Jul 15;12:30. doi: 10.1186/s12970-015-0090-y. eCollection 2015. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2015. PMID: 26175657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ocular growth and metabolomics are dependent upon the spectral content of ambient white light.Sci Rep. 2021 Apr 7;11(1):7586. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87201-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33828194 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of Selected Antioxidative and Bioactive Compounds in Meat and Animal Origin Products.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Aug 22;8(9):335. doi: 10.3390/antiox8090335. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31443517 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dunnett M, Harris RC. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of imidazole dipeptides, histidine, 1-methylhistidine and 3-methylhistidine in equine and camel muscle and individual muscle fibres. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl. 1997;688:47–55. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4347(97)88054-1. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

