Centrobin regulates centrosome function in interphase cells by limiting pericentriolar matrix recruitment
- PMID: 23442802
- PMCID: PMC3637348
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.23879
Centrobin regulates centrosome function in interphase cells by limiting pericentriolar matrix recruitment
Abstract
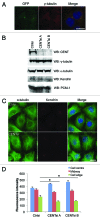
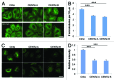
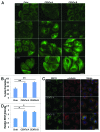
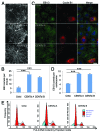
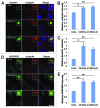
The amount of pericentriolar matrix at the centrosome is tightly linked to both microtubule nucleation and centriole duplication, although the exact mechanism by which pericentriolar matrix levels are regulated is unclear. Here we show that Centrobin, a centrosomal protein, is involved in regulating these levels. Interphase microtubule arrays in Centrobin-depleted cells are more focused around the centrosome and are less stable than the arrays in control cells. Centrobin-depleted cells initiate microtubule nucleation more rapidly than control cells and exhibit an increase in the number of growing microtubule ends emanating from the centrosome, while the parameters of microtubule plus end dynamics around the centrosome are not significantly altered. Finally, we show that Centrobin depletion results in the increased recruitment of pericentriolar matrix proteins to the centrosome, including γ-tubulin, AKAP450, Kendrin and PCM-1. We propose that Centrobin might regulate microtubule nucleation and organization by controlling the amount of pericentriolar matrix.
Keywords: centriole duplication; centrobin; microtubules; nucleation; pericentriolar matrix.
Figures
Comment in
-
More isn't always better: limiting centrosome size in interphase.Cell Cycle. 2013 May 15;12(10):1482. doi: 10.4161/cc.24853. Epub 2013 Apr 29. Cell Cycle. 2013. PMID: 23652924 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
