Direct observation of protein unfolded state compaction in the presence of macromolecular crowding
- PMID: 23442920
- PMCID: PMC3566456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.12.020
Direct observation of protein unfolded state compaction in the presence of macromolecular crowding
Abstract
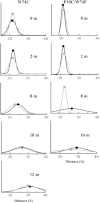
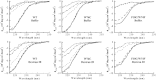
Proteins fold and function in cellular environments that are crowded with other macromolecules. As a consequence of excluded volume effects, compact folded states of proteins should be indirectly stabilized due to destabilization of extended unfolded conformations. Here, we assess the role of excluded volume in terms of protein stability, structural dimensions and folding dynamics using a sugar-based crowding agent, dextran 20, and the small ribosomal protein S16 as a model system. To specifically address dimensions, we labeled the protein with BODIPY at two positions and measured Trp-BODIPY distances under different conditions. As expected, we found that dextran 20 (200 mg/ml) stabilized the variants against urea-induced unfolding. At conditions where the protein is unfolded, Förster resonance energy transfer measurements reveal that in the presence of dextran, the unfolded ensemble is more compact and there is residual structure left as probed by far-ultraviolet circular dichroism. In the presence of a crowding agent, folding rates are faster in the two-state regime, and at low denaturant concentrations, a kinetic intermediate is favored. Our study provides direct evidence for protein unfolded-state compaction in the presence of macromolecular crowding along with its energetic and kinetic consequences.
Copyright © 2013 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Macromolecular crowding effects on two homologs of ribosomal protein s16: protein-dependent structural changes and local interactions.Biophys J. 2014 Jul 15;107(2):401-410. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.05.038. Biophys J. 2014. PMID: 25028882 Free PMC article.
-
Extreme temperature tolerance of a hyperthermophilic protein coupled to residual structure in the unfolded state.J Mol Biol. 2008 Jun 13;379(4):845-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.04.007. Epub 2008 Apr 8. J Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18471828
-
Unfolded states under folding conditions accommodate sequence-specific conformational preferences with random coil-like dimensions.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jun 18;116(25):12301-12310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1818206116. Epub 2019 Jun 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31167941 Free PMC article.
-
Folding, stability and shape of proteins in crowded environments: experimental and computational approaches.Int J Mol Sci. 2009 Feb;10(2):572-588. doi: 10.3390/ijms10020572. Epub 2009 Feb 13. Int J Mol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19333422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of macromolecular crowding agents on protein folding in vitro and in silico.Biophys Rev. 2013 Jun;5(2):137-145. doi: 10.1007/s12551-013-0108-0. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Biophys Rev. 2013. PMID: 28510156 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Atomistic Modeling of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins Under Polyethylene Glycol Crowding: Quantitative Comparison with Experimental Data and Implication of Protein-Crowder Attraction.J Phys Chem B. 2018 Dec 13;122(49):11262-11270. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b07066. Epub 2018 Oct 3. J Phys Chem B. 2018. PMID: 30230839 Free PMC article.
-
All atom insights into the impact of crowded environments on protein stability by NMR spectroscopy.Nat Commun. 2020 Nov 13;11(1):5760. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19616-w. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 33188202 Free PMC article.
-
Simulations of a protein fold switch reveal crowding-induced population shifts driven by disordered regions.Commun Chem. 2023 Sep 9;6(1):191. doi: 10.1038/s42004-023-00995-2. Commun Chem. 2023. PMID: 37689829 Free PMC article.
-
Quantification of Entropic Excluded Volume Effects Driving Crowding-Induced Collapse and Folding of a Disordered Protein.J Phys Chem Lett. 2022 Apr 7;13(13):3112-3120. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c00316. Epub 2022 Mar 31. J Phys Chem Lett. 2022. PMID: 35357183 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between Alpha-Synuclein and Other Human and Non-Human Amyloidogenic Proteins: Consequences for Amyloid Formation in Parkinson's Disease.J Parkinsons Dis. 2020;10(3):819-830. doi: 10.3233/JPD-202085. J Parkinsons Dis. 2020. PMID: 32538869 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Matouschek A., Kellis J.T., Jr., Fersht A.R. Mapping the transition state and pathway of protein folding by protein engineering. Nature. 1989;340:122–126. - PubMed
-
- Bryngelson J.D., Onuchic J.N., Wolynes P.G. Funnels, pathways, and the energy landscape of protein folding: a synthesis. Proteins. 1995;21:167–195. - PubMed
-
- Ellis R.J., Minton A.P. Cell biology: join the crowd. Nature. 2003;425:27–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

