Recent advances in vaccine development for herpes simplex virus types I and II
- PMID: 23442925
- PMCID: PMC3903888
- DOI: 10.4161/hv.23289
Recent advances in vaccine development for herpes simplex virus types I and II
Abstract
Despite recent advances in vaccine design and strategies, latent infection with herpes simplex virus (HSV) remains a formidable challenge. Approaches involving live-attenuated viruses and inactivated viral preparations were popular throughout the twentieth century. In the past ten years, many vaccine types, both prophylactic or therapeutic, have contained a replication-defective HSV, viral DNA or glycoproteins. New research focused on the mechanism of immune evasion by the virus has involved developing vaccines with various gene deletions and manipulations combined with the use of new and more specific adjuvants. In addition, new "prime-boost" methods of strengthening the vaccine efficacy have proven effective, but there have also been flaws with some recent strategies that appear to have compromised vaccine efficacy in humans. Given the complicated lifecycle of HSV and its unique way of spreading from cell-to-cell, it can be concluded that the development of an ideal vaccine needs new focus on cell-mediated immunity, better understanding of the latent viral genome and serious consideration of gender-based differences in immunity development among humans. This review summarizes recent developments made in the field and sheds light on some potentially new ways to conquer the problem including development of dual-action prophylactic microbicides that prohibit viral entry and, in addition, induce a strong antigen response.
Keywords: T cells; adjuvant; asymptomatic; humoral; immunity; seronegative; seropositive; symptomatic.
Figures
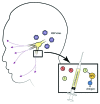
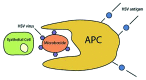
References
-
- Brittle EE, Friedman HM. Current herpes simplex virus vaccine approaches - a short review. US Infectious Diseases. 2006;1:13–6.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
