Structure prediction, molecular dynamics simulation and docking studies of D-specific dehalogenase from Rhizobium sp. RC1
- PMID: 23443090
- PMCID: PMC3546658
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms131215724
Structure prediction, molecular dynamics simulation and docking studies of D-specific dehalogenase from Rhizobium sp. RC1
Abstract
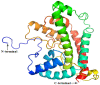
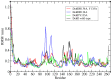
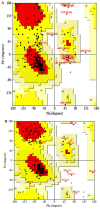
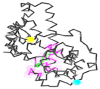
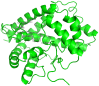
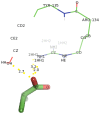
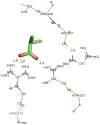
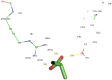
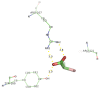
Currently, there is no three-dimensional structure of D-specific dehalogenase (DehD) in the protein database. We modeled DehD using ab initio technique, performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and docking of D-2-chloropropionate (D-2CP), D-2-bromopropionate (D-2BP), monochloroacetate (MCA), monobromoacetate (MBA), 2,2-dichloropropionate (2,2-DCP), d,l-2,3-dichloropropionate (d,l-2,3-DCP), and 3-chloropropionate (3-CP) into the DehD active site. The sequences of DehD and D-2-haloacid dehalogenase (HadD) from Pseudomonas putida AJ1 have 15% sequence similarity. The model had 80% of the amino acid residues in the most favored region when compared to the crystal structure of DehI from Pseudomonas putida PP3. Docking analysis revealed that Arg107, Arg134 and Tyr135 interacted with D-2CP, and Glu20 activated the water molecule for hydrolytic dehalogenation. Single residue substitutions at 25-30 °C showed that polar residues of DehD were stable when substituted with nonpolar residues and showed a decrease in activity within the same temperature range. The molecular dynamics simulation of DehD and its variants showed that in R134A variant, Arg107 interacted with D-2CP, while in Y135A, Gln221 and Arg231 interacted with D-2CP. It is our emphatic belief that the new model will be useful for the rational design of DehDs with enhanced potentials.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Insights into the stereospecificity of the d-specific dehalogenase from Rhizobium sp. RC1 toward d- and l-2-chloropropionate.Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014 Jul 4;28(4):608-615. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2014.937907. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014. PMID: 26740767 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of non-natural halogenated substrates with D-specific dehalogenase (DehD) mutants using in silico studies.Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014 Sep 3;28(5):949-957. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2014.960663. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014. PMID: 26019583 Free PMC article.
-
Theoretical analyses on enantiospecificity of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase (DehL) from Rhizobium sp. RC1 towards 2-chloropropionic acid.J Mol Graph Model. 2019 Nov;92:131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2019.07.012. Epub 2019 Jul 21. J Mol Graph Model. 2019. PMID: 31352207
-
l-2-Haloacid dehalogenase (DehL) from Rhizobium sp. RC1.Springerplus. 2016 May 20;5(1):695. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2328-9. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27347470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial hydrolytic dehalogenases and related enzymes: occurrences, reaction mechanisms, and applications.Chem Rec. 2008;8(2):67-74. doi: 10.1002/tcr.20141. Chem Rec. 2008. PMID: 18366103 Review.
Cited by
-
Inverting hydrolases and their use in enantioconvergent biotransformations.Trends Biotechnol. 2013 Aug;31(8):468-78. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Trends Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23809848 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the stereospecificity of the d-specific dehalogenase from Rhizobium sp. RC1 toward d- and l-2-chloropropionate.Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014 Jul 4;28(4):608-615. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2014.937907. Epub 2014 Oct 23. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014. PMID: 26740767 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico Analysis on the Interaction of Haloacid Dehalogenase from Bacillus cereus IndB1 with 2-Chloroalkanoic Acid Substrates.ScientificWorldJournal. 2022 Oct 8;2022:1579194. doi: 10.1155/2022/1579194. eCollection 2022. ScientificWorldJournal. 2022. PMID: 36254337 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the molecular mechanism of dehalogenation catalyzed by D-2-haloacid dehalogenase from crystal structures.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 23;8(1):1454. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-19050-x. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29362453 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of non-natural halogenated substrates with D-specific dehalogenase (DehD) mutants using in silico studies.Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014 Sep 3;28(5):949-957. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2014.960663. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014. PMID: 26019583 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slater J.H., Bull A.T., Hardman D.J. Microbial dehalogenation of halogenated alkanoic acids, alcohols and alkanes. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 1997;38:133–176. - PubMed
-
- Weightman A.J., Topping A.W., Hill K.E., Lee L.L., Sakai K., Slater J.H., Thomas A.W. Transposition of DEH, a broad-host-range transposon flanked by ISPpu12, in Pseudomonas putida is associated with genomic rearrangements and dehalogenase gene silencing. J. Bacteriol. 2002;184:6581–6591. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Janssen D.B., Oppentocht J.E., Poelarends G.J. Microbial dehalogenation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2001;12:254–258. - PubMed
-
- Ridder I.S., Rozeboom H.J., Kalk K.H., Dijkstra B.W. Crystal structures of intermediates in the dehalogenation of haloalkanoates by L-2-haloacid dehalogenase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:30672–30678. - PubMed
-
- Li Y.-F., Hata Y., Fujii T., Hisano T., Nishihara M., Kurihara T., Esaki N. Crystal structures of reaction intermediates of L-2-haloacid dehalogenase and implications for the reaction mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:15035–15044. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

