Transvaginal electrical stimulation with surface-EMG biofeedback in managing stress urinary incontinence in women of premenopausal age: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 23443345
- PMCID: PMC3779318
- DOI: 10.1007/s00192-013-2071-5
Transvaginal electrical stimulation with surface-EMG biofeedback in managing stress urinary incontinence in women of premenopausal age: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction and hypothesis: The aim of this study was to evaluate the results of conservative treatment of urodynamic stress urinary incontinence (SUI) using transvaginal electrical stimulation with surface-electromyography-assisted biofeedback (TVES + sEMG) in women of premenopausal age.
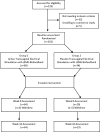
Methods: One hundred and two patients with SUI were divided into two groups: active (n = 68) and placebo (n = 34) TVES + sEMG. The treatment lasted for 8 weeks and consisted of two sessions per day. Women were evaluated before and after the intervention by pad test, voiding diary, urodynamic test, and the Incontinence Quality of Life Questionnaire (I-QOL).
Results: Mean urinary leakage on a standard pad test at the end of 8th week was significantly lower in the active than the placebo group (19.5 ± 13.6 vs. 39.8 ± 28.5). Mean urinary leakage on a 24-h pad test was significantly reduced in the active group at the end of 8th and 16th weeks compared with the placebo group (8.2 ± 14.8 vs. 14.6 ± 18.9 and 6.1 ± 11.4 vs. 18.2 ± 20.8, respectively). There was also a significant improvement in muscle strength as measured by the Oxford scale in the active vs the placebo group after 8 and 16 weeks (4.2 vs 2.6 and 4.1 vs 2.7, respectively). No significant difference was found between groups in urodynamic data before and after treatment. At the end of 8th week, the mean I-QOL score in the active vs the placebo group was 78.2 ± 17.9 vs 55.9 ± 14.2, respectively, and at the end of 16th week 80.8 ± 24.1 vs. 50.6 ± 14.9, respectively.
Conclusion: Our study showed that TVES + sEMG is a trustworthy method of treatment in premenopausal women with SUI; however, its reliability needs to be established.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical