Identification of cell-surface molecular interactions under living conditions by using the enzyme-mediated activation of radical sources (EMARS) method
- PMID: 23443365
- PMCID: PMC3571769
- DOI: 10.3390/s121216037
Identification of cell-surface molecular interactions under living conditions by using the enzyme-mediated activation of radical sources (EMARS) method
Abstract
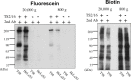
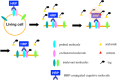
Important biological events associated with plasma membranes, such as signal transduction, cell adhesion, and protein trafficking, are mediated through the membrane microdomains. We have developed a novel method termed enzyme-mediated activation of radical sources (EMARS) to identify coclustering molecules on the cell surface under living conditions, which features a radical formation from an aryl azide reagent by horseradish peroxidase (HRP). For identification of molecules labeled by the EMARS reaction, antibody array system and mass spectrometry-based proteomics approaches are available. Spatio- temporally-regulated interaction between b1 integrin and ErbB4 involved in fibronectin-dependent cell migration and therapeutic antibody-stimulated interaction between FGFR3 and CD20 were discovered using the EMARS method.
Figures





References
-
- Jacobson K., Mouritsen O.G., Anderson R.G. Lipid rafts: At a crossroad between cell biology and physics. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007;9:7–14. - PubMed
-
- Sheets E.D., Lee G.M., Simson R., Jacobson K. Transient confinement of a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein in the plasma membrane. Biochemistry. 1997;36:12449–12458. - PubMed
-
- Vereb G., Matkó J., Vámosi G., Ibrahim S., Magyar E., Varga S., Szöllosi J., Jenei A., Gáspár R.J., Waldmann T., Damjanovich S. Cholesterol-dependent clustering of IL-2Ralpha and its colocalization with HLA and CD48 on T lymphoma cells suggest their functional association with lipid rafts. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:6013–6018. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

