Selenoprotein K is required for palmitoylation of CD36 in macrophages: implications in foam cell formation and atherogenesis
- PMID: 23444136
- PMCID: PMC3629442
- DOI: 10.1189/jlb.1212647
Selenoprotein K is required for palmitoylation of CD36 in macrophages: implications in foam cell formation and atherogenesis
Abstract
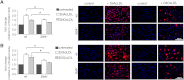
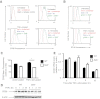
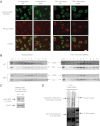
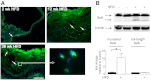
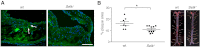
Selk is an ER transmembrane protein important for calcium flux and macrophage activation, but its role in foam cell formation and atherosclerosis has not been evaluated. BMDMs from Selk(-/-) mice exhibited decreased uptake of modLDL and foam cell formation compared with WT controls, and the differences were eliminated with anti-CD36 blocking antibody. CD36 expression was decreased in TNF-α-stimulated Selk(-/-) BMDMs compared with WT controls. Fluorescence microscopy revealed TNF-α-induced clustering of CD36 in WT BMDMs indicative of lipid raft localization, which was absent in Selk(-/-) BMDMs. Fractionation revealed lower levels of CD36 reaching lipid rafts in TNF-α-stimulated Selk(-/-) BMDMs. Immunoprecipitation showed that Selk(-/-) BMDMs have decreased CD36 palmitoylation, which occurs at the ER membrane and is crucial for stabilizing CD36 expression and directing its localization to lipid rafts. To assess if this phenomenon had a role in atherogenesis, a HFD was fed to irradiated Ldlr(-/-) mice reconstituted with BM from Selk(-/-) or WT mice. Selk was detected in aortic plaques of controls, particularly in macrophages. Selk(-/-) in immune cells led to reduction in atherosclerotic lesion formation without affecting leukocyte migration into the arterial wall. These findings suggest that Selk is important for stable, localized expression of CD36 in macrophages during inflammation, thereby contributing to foam cell formation and atherogenesis.
Figures


References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D., Adams R. J., Brown T. M., Carnethon M., Dai S., De Simone G., Ferguson T. B., Ford E., Furie K., Gillespie C.., et al. (2010) Heart disease and stroke statistics—2010 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 121, e46–e215 - PubMed
-
- Hansson G. K., Robertson A. K., Soderberg-Naucler C. (2006) Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Ann. Rev. Pathol. 1, 297–329 - PubMed
-
- Weber C., Zernecke A., Libby P. (2008) The multifaceted contributions of leukocyte subsets to atherosclerosis: lessons from mouse models. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 802–815 - PubMed
-
- Hansson G. K., Libby P. (2006) The immune response in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 6, 508–519 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AI089999/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01AI089999/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- G12MD007601/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075677/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20GM103516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL081663/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G12RR003061/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103341/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR016453/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003061/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007601/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL075677/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR016453/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL081663/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AT004844/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- R21AT004844/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

