Variation in prescribing patterns and therapeutic drug monitoring of intravenous busulfan in pediatric hematopoietic cell transplant recipients
- PMID: 23444282
- PMCID: PMC5007875
- DOI: 10.1177/0091270012447196
Variation in prescribing patterns and therapeutic drug monitoring of intravenous busulfan in pediatric hematopoietic cell transplant recipients
Abstract
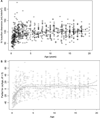
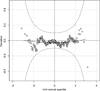
Personalizing intravenous (IV) busulfan doses in children using therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is an integral component of hematopoietic cell transplant. The authors sought to characterize initial dosing and TDM of IV busulfan, along with factors associated with busulfan clearance, in 729 children who underwent busulfan TDM from December 2005 to December 2008. The initial IV busulfan dose in children weighing ≤12 kg ranged 4.8-fold, with only 19% prescribed the package insert dose of 1.1 mg/kg. In those children weighing >12 kg, the initial dose ranged 5.4-fold, and 79% were prescribed the package insert dose. The initial busulfan dose achieved the target exposure in only 24.3% of children. A wide range of busulfan exposures were targeted for children with the same disease (eg, 39 target busulfan exposures for the 264 children diagnosed with acute myeloid leukemia). Considerable heterogeneity exists regarding when TDM is conducted and the number of pharmacokinetic samples obtained. Busulfan clearance varied by age and dosing frequency but not by underlying disease. The authors- group is currently evaluating how using population pharmacokinetics to optimize initial busulfan dose and TDM (eg, limited sampling schedule in conjunction with maximum a posteriori Bayesian estimation) may affect clinical outcomes in children.
© The Author(s) 2013.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests Dr McCune has received research funding from Otsuka Pharmaceutical of North America.
Figures


References
-
- Deeg HJ, Maris MB, Scott BL, Warren EH. Optimization of allogeneic transplant conditioning: not the time for dogma. Leukemia. 2006;20(10):1701–1705. - PubMed
-
- McCune JS, Holmberg LA. Busulfan in hematopoietic stem cell transplant setting. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2009;5(8):957–969. - PubMed
-
- Slattery JT, Clift RA, Buckner CD, et al. Marrow transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia: the influence of plasma busulfan levels on the outcome of transplantation. Blood. 1997;89(8):3055–3060. - PubMed
-
- Woods WG, Kobrinsky N, Buckley JD, et al. Timed-sequential induction therapy improves postremission outcome in acute myeloid leukemia: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. Blood. 1996;87(12):4979–4989. - PubMed
-
- Slattery JT, Sanders JE, Buckner CD, et al. Graft-rejection and toxicity following bone marrow transplantation in relation to busulfan pharmacokinetics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;16(1):31–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

